Acute and chronic effects of SGLT2 blockade on glomerular and tubular function in the early diabetic rat
- PMID: 21940401
- PMCID: PMC3349378
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpregu.00357.2011
Acute and chronic effects of SGLT2 blockade on glomerular and tubular function in the early diabetic rat
Abstract
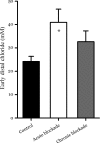
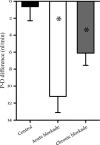
Tubuloglomerular feedback (TGF) stabilizes nephron function from minute to minute and adapts to different steady-state inputs to maintain this capability. Such adaptation inherently renders TGF less efficient at buffering long-term disturbances, but the magnitude of loss is unknown. We undertook the present study to measure the compromise between TGF and TGF adaptation in transition from acute to chronic decline in proximal reabsorption (Jprox). As a tool, we blocked proximal tubule sodium-glucose cotransport with the SGLT2 blocker dapagliflozin in hyperglycemic rats with early streptozotocin diabetes, a condition in which a large fraction of proximal fluid reabsorption owes to SGLT2. Dapagliflozin acutely reduced proximal reabsorption leading to a 70% increase in early distal chloride, a saturated TGF response, and a major reduction in single nephron glomerular filtration rate (SNGFR). Acute and chronic effects on Jprox were indistinguishable. Adaptations to 10-12 days of dapagiflozin included increased reabsorption by Henle's loop, which caused a partial relaxation in the increased tone exerted by TGF that could be explained without desensitization of TGF. In summary, TGF contributes to long-term fluid and salt balance by mediating a persistent decline in SNGFR as the kidney adapts to a sustained decrease in Jprox.
Figures

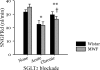






References
-
- Bonventre JF, Zuk A. Ischemic acute renal failure: An inflammatory disease? Kidney Int 66: 480– 485, 2004 - PubMed
-
- Brown R, Ollerstam A, Johansson B, Skott O, Gebre-Medhin S, Fredholm B, Persson AE. Abolished tubuloglomerular feedback, and increased plasma renin in adenosine A1 receptor-deficient mice. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 281: R1362– R1367, 2001 - PubMed
-
- Deng A, Hammes JS, Thomson SC. Hemodynamics of early tubuloglomerular feedback resetting during reduced proximal reabsorption. Kidney Int 62: 2136– 2143, 2001 - PubMed
-
- Goldwasser P, Fotino S. Acute renal failure following massive mannitol infusion. Appropriate response of tubuloglomerular feedback? Arch Intern Med 144: 2214– 2116, 1984 - PubMed
-
- Guyton AC, Coleman TG, Cowley AW, Manning RD, Norman RA, Ferguson JD. Brief reviews: a systems analysis approach to understanding long-range arterial blood pressure control and hypertension. Circ Res 35: 159– 176, 1974
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

