Linkage of gut microbiome with cognition in hepatic encephalopathy
- PMID: 21940902
- PMCID: PMC3345956
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpgi.00190.2011
Linkage of gut microbiome with cognition in hepatic encephalopathy
Abstract
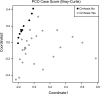
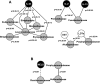
Hepatic encephalopathy (HE) has been related to gut bacteria and inflammation in the setting of intestinal barrier dysfunction. We aimed to link the gut microbiome with cognition and inflammation in HE using a systems biology approach. Multitag pyrosequencing (MTPS) was performed on stool of cirrhotics and age-matched controls. Cirrhotics with/without HE underwent cognitive testing, inflammatory cytokines, and endotoxin analysis. Patients with HE were compared with those without HE using a correlation-network analysis. A select group of patients with HE (n = 7) on lactulose underwent stool MTPS before and after lactulose withdrawal over 14 days. Twenty-five patients [17 HE (all on lactulose, 6 also on rifaximin) and 8 without HE, age 56 ± 6 yr, model for end-stage liver disease score 16 ± 6] and ten controls were included. Fecal microbiota in cirrhotics were significantly different (higher Enterobacteriaceae, Alcaligeneceae, and Fusobacteriaceae and lower Ruminococcaceae and Lachnospiraceae) compared with controls. We found altered flora (higher Veillonellaceae), poor cognition, endotoxemia, and inflammation (IL-6, TNF-α, IL-2, and IL-13) in HE compared with cirrhotics without HE. In the cirrhosis group, Alcaligeneceae and Porphyromonadaceae were positively correlated with cognitive impairment. Fusobacteriaceae, Veillonellaceae, and Enterobacteriaceae were positively and Ruminococcaceae negatively related to inflammation. Network-analysis comparison showed robust correlations (all P < 1E-5) only in the HE group between the microbiome, cognition, and IL-23, IL-2, and IL-13. Lactulose withdrawal did not change the microbiome significantly beyond Fecalibacterium reduction. We concluded that cirrhosis, especially when complicated with HE, is associated with significant alterations in the stool microbiome compared with healthy individuals. Specific bacterial families (Alcaligeneceae, Porphyromonadaceae, Enterobacteriaceae) are strongly associated with cognition and inflammation in HE.
Figures
References
-
- Bajaj JS. Review article: the modern management of hepatic encephalopathy. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 31: 537– 547, 2010. . - PubMed
-
- Bajaj JS, Hafeezullah M, Franco J, Varma RR, Hoffmann RG, Knox JF, Hischke D, Hammeke TA, Pinkerton SD, Saeian K. Inhibitory control test for the diagnosis of minimal hepatic encephalopathy. Gastroenterology 135: 1591– 1600, 2008. . - PubMed
-
- Bajaj JS, Heuman DM, Wade JB, Gibson DP, Saeian K, Wegelin JA, Hafeezullah M, Bell DE, Sterling RK, Stravitz RT, Fuchs M, Luketic V, Sanyal AJ. Rifaximin improves driving simulator performance in a randomized trial of patients with minimal hepatic encephalopathy. Gastroenterology 140: 478– 487, 2011. . - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

