Siblings with ischemic stroke study: results of a genome-wide scan for stroke loci
- PMID: 21940970
- PMCID: PMC3251509
- DOI: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.111.620484
Siblings with ischemic stroke study: results of a genome-wide scan for stroke loci
Erratum in
- Stroke. 2013 Sep;44(9):e117
Abstract
Background and purpose: Ischemic stroke has a strong familial component to risk. The Siblings With Ischemic Stroke Study (SWISS) is a genome-wide, family-based analysis that included use of imputed genotypes. The Siblings With Ischemic Stroke Study was conducted to examine the associations between single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and risk of stroke and stroke subtypes within pairs.
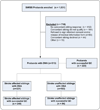
Methods: The Siblings With Ischemic Stroke Study enrolled 312 probands with ischemic stroke from 70 US and Canadian centers. Affected siblings were ascertained by centers and confirmed by central record review; unaffected siblings were ascertained by telephone contact. Ischemic stroke was subtyped according to Trial of Org 10172 in Acute Stroke Treatment criteria. Genotyping was performed with an Illumina 610 quad array (probands) and an Illumina linkage V array (affected siblings). SNPs were imputed by using 1000 Genomes Project data and MACH software. Family-based association analyses were conducted by using the sibling transmission-disequilibrium test.
Results: For all pairs, the correlation of age at stroke within pairs of affected siblings was r=0.83 (95% CI, 0.78-0.86; P<2.2×10(-16)). The correlation did not differ substantially by subtype. The concordance of stroke subtypes among affected pairs was 33.8% (kappa=0.13; P=5.06×10(-4)) and did not differ by age at stroke in the proband. Although no SNP achieved genome-wide significance for risk of ischemic stroke, there was clustering of the most associated SNPs on chromosomes 3p (neuronal nitric oxide synthase) and 6p.
Conclusions: Stroke subtype and age at stroke in affected sibling pairs exhibit significant clustering. No individual SNP reached genome-wide significance. However, 2 promising candidate loci were identified, including 1 that contains neuronal nitric oxide synthase, although these risk loci warrant further examination in larger sample collections.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest/Disclosure
The funding source had no involvement in study design beyond peer review of the grant. The funding source had no involvement in collection, analysis, or interpretation of data; in writing of the report; or in the decision to submit the article for publication.
Figures

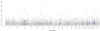
Comment in
-
Identifying the genetic contribution to ischemic stroke: in small steps to success.Stroke. 2011 Oct;42(10):2716-7. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.111.629758. Epub 2011 Sep 22. Stroke. 2011. PMID: 21940977 No abstract available.
References
-
- The World Health Organization MONICA Project (monitoring trends and determinants in cardiovascular disease): a major international collaboration. WHO MONICA Project Principal Investigators. J Clin Epidemiol. 1988;41:105–114. - PubMed
-
- Adams HP, Jr, Bendixen BH, Kappelle LJ, Biller J, Love BB, Gordon DL, 3rd, et al. Classification of subtype of acute ischemic stroke. Definitions for use in a multicenter clinical trial. TOAST. Trial of Org 10172 in Acute Stroke Treatment. Stroke. 1993;24:35–41. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

