Overweight and obesity in eastern mediterranean region: prevalence and possible causes
- PMID: 21941635
- PMCID: PMC3175401
- DOI: 10.1155/2011/407237
Overweight and obesity in eastern mediterranean region: prevalence and possible causes
Abstract
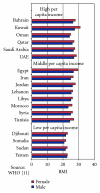
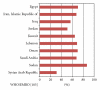
The objective of this paper was to explore the prevalence of overweight and obesity among various age groups as well as discuss the possible factors that associated with obesity in the Eastern Mediterranean Region (EMR). A systematic review of published papers between 1990 and 2011 was carried out. Obesity reached an alarming level in all age groups of the EMR countries. The prevalence of overweight among preschool children(<5 years) ranged from 1.9% to 21.9%, while the prevalence of overweight and obesity among school children ranged from 7% to 45%. Among adults the prevalence of overweight and obesity ranged from 25% to 81.9%. Possible factors determining obesity in this region include: nutrition transition, inactivity, urbanization, marital status, a shorter duration of breastfeeding, frequent snacking, skipping breakfast, a high intake of sugary beverages, an increase in the incidence of eating outside the home, long periods of time spent viewing television, massive marketing promotion of high fat foods, stunting, perceived body image, cultural elements and food subsidize policy. A national plan of action to overcome obesity is urgently needed to reduce the economic and health burden of obesity in this region.
Figures
References
-
- Musaiger AO. Overweight and obesity in the Eastern Mediterranean Region: can we control it? Eastern Mediterranean Health Journal. 2004;10(6):789–793. - PubMed
-
- Sibai AM, Nasreddine L, Mokdad AH, Adra N, Tabet M, Hwalla N. Nutrition transition and cardiovascular disease risk factors in Middle East and North Africa countries: reviewing the evidence. Annals of Nutrition and Metabolism. 2010;57(3-4):193–203. - PubMed
-
- Ogden CL, Yanovski SZ, Carroll MD, Flegal KM. The epidemiology of obesity. Gastroenterology. 2007;132(6):2087–2102. - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization (WHO) WHO Technical Report Series. 894. Geneva, Switzerland: WHO; 1998. Obesity and managing the global epidemic. - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization (WHO) WHO Technical Report Series. 854. Geneva, Switzerland: WHO; 1995. Physical status: the use and interpretation of anthropometry. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources