Uniting germline and stem cells: the function of Piwi proteins and the piRNA pathway in diverse organisms
- PMID: 21942366
- PMCID: PMC3832951
- DOI: 10.1146/annurev-genet-110410-132541
Uniting germline and stem cells: the function of Piwi proteins and the piRNA pathway in diverse organisms
Abstract
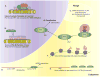
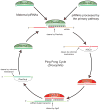
The topipotency of the germline is the full manifestation of the pluri- and multipotency of embryonic and adult stem cells, thus the germline and stem cells must share common mechanisms that guarantee their multipotentials in development. One of the few such known shared mechanisms is represented by Piwi proteins, which constitute one of the two subfamilies of the Argonaute protein family. Piwi proteins bind to Piwi-interacting RNAs (piRNAs) that are generally 26 to 31 nucleotides in length. Both Piwi proteins and piRNAs are most abundantly expressed in the germline. Moreover, Piwi proteins are expressed broadly in certain types of somatic stem/progenitor cells and other somatic cells across animal phylogeny. Recent studies indicate that the Piwi-piRNA pathway mediates epigenetic programming and posttranscriptional regulation, which may be responsible for its function in germline specification, gametogenesis, stem cell maintenance, transposon silencing, and genome integrity in diverse organisms.
Figures

References
-
- Agata K, Nakajima E, Funayama N, Shibata N, Saito Y, Umesono Y. Two different evolutionary origins of stem cell systems and their molecular basis. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2006;17:503–9. - PubMed
-
- Alie A, Leclere L, Jager M, Dayraud C, Chang P, et al. Somatic stem cells express Piwi and Vasa genes in an adult ctenophore: Ancient association of “germline genes” with stemness. Dev Biol. 2011;350:183–97. - PubMed
-
- Aravin A, Gaidatzis D, Pfeffer S, Lagos-Quintana M, Landgraf P, et al. A novel class of small RNAs bind to MILI protein in mouse testes. Nature. 2006;442:203–7. - PubMed
-
- Aravin AA, Sachidanandam R, Girard A, Fejes-Toth K, Hannon GJ. Developmentally regulated piRNA clusters implicate MILI in transposon control. Science. 2007;316:744–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

