DIABRISK-SL prevention of cardio-metabolic disease with life style modification in young urban Sri Lankan's--study protocol for a randomized controlled trial
- PMID: 21943067
- PMCID: PMC3197497
- DOI: 10.1186/1745-6215-12-209
DIABRISK-SL prevention of cardio-metabolic disease with life style modification in young urban Sri Lankan's--study protocol for a randomized controlled trial
Abstract
Background: Urban South-Asian's are predisposed to early onset of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) and cardiovascular disease (CVD). There is an urgent need for country specific primary prevention strategies to address the growing burden of cardio-metabolic disease in this population. The aim of this clinical trial is to evaluate whether intensive (3-monthly) lifestyle modification advice is superior to a less-intensive (12 monthly; control group) lifestyle modification advice on a primary composite cardio-metabolic end point in 'at risk' urban subjects aged between 5-40 years.
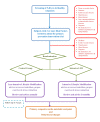
Methods/design: This is an open randomised controlled parallel group clinical trial performed at a single centre in Colombo, Sri-Lanka. A cluster sampling strategy was used to select a large representative sample of subjects aged between 5-40 years at high risk of T2DM and CVD for the intervention study. We have screened 23,298 (males 47% females 53%) healthy subjects for four risk factors: obesity, elevated waist circumference, family history of diabetes and physical inactivity, using a questionnaire and anthropometry. Those with two or more risk-factors were recruited to the intervention trial. We aim to recruit 4600 subjects for the intervention trial. The primary composite cardio-metabolic end point is; new onset T2DM, impaired glucose tolerance, impaired fasting glycaemia, new onset hypertension and albuminuria, following 5 years of intervention. The effect of the intervention on pre-specified secondary endpoints will also be evaluated. The study will be conducted according to good clinical and ethical practice, data analysis and reporting guidelines.
Discussion: DIABRISK-SL is a large population based trial to evaluate the prevalence of diabetes, pre-diabetes and cardio-metabolic risk factors among young urban Sri-Lankans and the effect of a primary prevention strategy on cardio-metabolic disease end points. This work will enable country specific and regional cardio-metabolic risk scores to be derived. Further if the proposed intervention is successful the results of this study can be translated and implemented as a low-cost primary prevention tool in Sri-Lanka and other low/middle income developing countries.
Trial registration: The trial is registered with the World Health Organisation and Sri-Lanka clinical trial registry number SLCTR/2008/003.
Figures
References
-
- Ramachandran A, Ma RCW, Snehalatha C. Diabetes in Asia. Lancet. 2010;30:408–18. 375. - PubMed
-
- Sicree R, Shaw J, Zimmet P. In: Diabetes Atlas. 3. Gan D, editor. International Diabetes Federation, Brussels; 2006. Prevalence and projections; pp. 16–104.
-
- Department of Census and Statistics. Census Report - 2001, Ministry of Finance and Planning, Sri Lanka; 2001.
-
- Katulanda P, Constantine GR, Mahesh JG, Sheriff R, Seneviratne RDA, Wijeratne S, Wijesuriya M, McCarthy MI, Adler AI, Matthews DR. Diabetic Medicine. Vol. 25. Cardiovascular Study (SLDCS); 2008. Prevalence and projections of diabetes and pre-diabetes in adults in Sri Lanka--Sri Lanka Diabetes; pp. 1062–9. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical