Regulation of AMPA receptor function by the human memory-associated gene KIBRA
- PMID: 21943600
- PMCID: PMC3200575
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2011.08.017
Regulation of AMPA receptor function by the human memory-associated gene KIBRA
Abstract
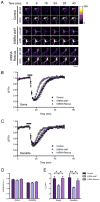
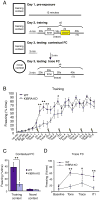
KIBRA has recently been identified as a gene associated with human memory performance. Despite the elucidation of the role of KIBRA in several diverse processes in nonneuronal cells, the molecular function of KIBRA in neurons is unknown. We found that KIBRA directly binds to the protein interacting with C-kinase 1 (PICK1) and forms a complex with α-amino-3-hydroxyl-5-methyl-4-isoxazole-propionate receptors (AMPARs), the major excitatory neurotransmitter receptors in the brain. KIBRA knockdown accelerates the rate of AMPAR recycling following N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor-induced internalization. Genetic deletion of KIBRA in mice impairs both long-term depression and long-term potentiation at hippocampal Schaffer collateral-CA1 synapses. Moreover, KIBRA knockout mice have severe deficits in contextual fear learning and memory. These results indicate that KIBRA regulates higher brain function by regulating AMPAR trafficking and synaptic plasticity.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


Comment in
-
Synaptic plasticity: Transporting memories.Nat Rev Neurosci. 2011 Oct 12;12(11):617. doi: 10.1038/nrn3127. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 21989193 No abstract available.
References
-
- Ashby MC, Ibaraki K, Henley JM. It's green outside: tracking cell surface proteins with pH-sensitive GFP. Trends Neurosci. 2004;27:257–261. - PubMed
-
- Bates TC, Price JF, Harris SE, Marioni RE, Fowkes FG, Stewart MC, Murray GD, Whalley LJ, Starr JM, Deary IJ. Association of KIBRA and memory. Neurosci Lett 2009 - PubMed
-
- Baumgartner R, Poernbacher I, Buser N, Hafen E, Stocker H. The WW domain protein Kibra acts upstream of Hippo in Drosophila. Dev Cell. 2010;18:309–316. - PubMed
-
- Buther K, Plaas C, Barnekow A, Kremerskothen J. KIBRA is a novel substrate for protein kinase Czeta. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2004;317:703–707. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

