GDE2 regulates subtype-specific motor neuron generation through inhibition of Notch signaling
- PMID: 21943603
- PMCID: PMC3183458
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2011.07.028
GDE2 regulates subtype-specific motor neuron generation through inhibition of Notch signaling
Abstract
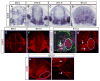
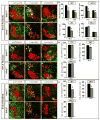
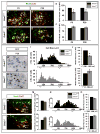
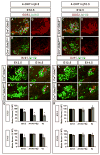
The specification of spinal interneuron and motor neuron identities initiates within progenitor cells, while motor neuron subtype diversification is regulated by hierarchical transcriptional programs implemented postmitotically. Here we find that mice lacking GDE2, a six-transmembrane protein that triggers motor neuron generation, exhibit selective losses of distinct motor neuron subtypes, specifically in defined subsets of limb-innervating motor pools that correlate with the loss of force-generating alpha motor neurons. Mechanistically, GDE2 is expressed by postmitotic motor neurons but utilizes extracellular glycerophosphodiester phosphodiesterase activity to induce motor neuron generation by inhibiting Notch signaling in neighboring motor neuron progenitors. Thus, neuronal GDE2 controls motor neuron subtype diversity through a non-cell-autonomous feedback mechanism that directly regulates progenitor cell differentiation, implying that subtype specification initiates within motor neuron progenitor populations prior to their differentiation into postmitotic motor neurons.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Arber S, Han B, Mendelsohn M, Smith M, Jessell TM, Sockanathan S. Requirement for the homeobox gene Hb9 in the consolidation of motor neuron identity. Neuron. 1999;23:659–674. - PubMed
-
- Arber S, Ladle DR, Lin JH, Frank E, Jessell TM. ETS gene Er81 controls the formation of functional connections between group Ia sensory afferents and motor neurons. Cell. 2000;101:485–498. - PubMed
-
- Burke RE, Strick PL, Kanda K, Kim CC, Walmsley B. Anatomy of medial gastrocnemius and soleus motor nuclei in cat spinal cord. J Neurophysiol. 1977;40:667–680. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

