White matter lesions and brain gray matter volume in cognitively normal elders
- PMID: 21943959
- PMCID: PMC3248984
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2011.08.010
White matter lesions and brain gray matter volume in cognitively normal elders
Abstract
Cerebral white matter lesions (WMLs) reflect small vessel disease, are common in elderly individuals, and are associated with cognitive impairment. We sought to determine the relationships between WMLs, age, gray matter (GM) volume, and cognition in the Cardiovascular Health Study (CHS). From the Cardiovascular Health Study we selected 740 cognitively normal controls with a 1.5 T magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan of the brain and a detailed diagnostic evaluation. WML severity was determined using a standardized visual rating system. GM volumes were analyzed using voxel-based morphometry implemented in the Statistical Parametric Mapping software. WMLs were inversely correlated with GM volume, with the greatest volume loss in the frontal cortex. Age-related atrophy was observed in the hippocampus and posterior cingulate cortex. Regression analyses revealed links among age, APOE*4 allele, hypertension, WMLs, GM volume, and digit symbol substitution test scores. Both advancing age and hypertension predict higher WML load, which is itself associated with GM atrophy. Longitudinal data are needed to confirm the temporal sequence of events leading to a decline in cognitive function.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure Statement - no actual or potential conflicts of interest.
Figures
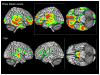
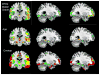
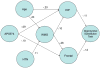
References
-
- Andresen EM, Malmgren JA, Carter WB, Patrick DL. Screening for depression in well older adults: evaluation of a short form of the CES-D (Center for Epidemiologic Studies Depression Scale) Am J Prev Med. 1994;10:77–84. - PubMed
-
- Appelman AP, Exalto LG, van der Graaf Y, Biessels GJ, Mali WP, Geerlings MI. White matter lesions and brain atrophy: more than shared risk factors? a systematic review. Cerebrovasc Dis. 2009;28(3):227–242. - PubMed
-
- Ashburner J, Friston KJ. Voxel-based morphometry - the methods. Neurol. 2000;11:805–821. - PubMed
-
- Baron RM, Kenny DA. The moderator-mediator variable distinction in social psychological research: conceptual, strategic, and statistical considerations. J Pers Soc Psychol. 1986;51:1173–1182. - PubMed
-
- Bartzokis G, Cummings JL, Syltzer D, Henderson VM, Nuechterlein KH, Mintz J. White matter structural integrity in healthy aging adults and patients with Alzheimer disease. Arch Neurol. 2003;60:393–398. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- N01 HC085086/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- AG15928/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC075150/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-85081/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R56 AG020098/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC085085/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-85086/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- AG05133/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-85079/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC045133/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-80007/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC085081/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CN015103/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG015928/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL080295/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC015103/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC085086/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC085083/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- AG020098/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC085082/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-85082/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC085080/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC-55222/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC055222/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC055222/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-055222/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC085079/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-85083/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-75150/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-85080/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG005133/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC085084/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- EB008281/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG020098/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EB008281/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC075150/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EB002172/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC035129/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

