Reflectance confocal microscopy for the diagnosis of eosinophilic esophagitis: a pilot study conducted on biopsy specimens
- PMID: 21944314
- PMCID: PMC3425354
- DOI: 10.1016/j.gie.2011.07.020
Reflectance confocal microscopy for the diagnosis of eosinophilic esophagitis: a pilot study conducted on biopsy specimens
Abstract
Background: Diagnosis of eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) currently requires endoscopic biopsy and histopathologic analysis of the biopsy specimens to count intraepithelial eosinophils. Reflectance confocal microscopy (RCM) is an endomicroscopy technology that is capable of obtaining high-resolution, optically sectioned images of esophageal mucosa without the administration of exogenous contrast.
Objective: In this study, we investigated the capability of a high-speed form of RCM, termed spectrally encoded confocal microscopy (SECM), to count intraepithelial esophageal eosinophils and characterize other microscopic findings of EoE.
Design: A total of 43 biopsy samples from 35 pediatric patients and 8 biopsy samples from 8 adult patients undergoing EGD for EoE were imaged by SECM immediately after their removal and then processed for routine histopathology. Two SECM readers, trained on adult cases, prospectively counted intraepithelial eosinophils and detected the presence of abscess, degranulation, and basal cell hyperplasia on SECM images from the pediatric patients. A pathologist blinded to the SECM data analyzed the same from corresponding slides.
Setting: The Gastrointestinal Unit, Massachusetts General Hospital.
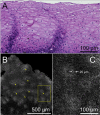
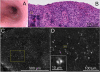
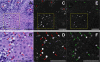
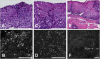
Results: Eosinophils by SECM demonstrated a higher reflectance than the surrounding cells and other inflammatory cells. There was good correlation between SECM and histology maximum eosinophil counts/high-power field (R = 0.76, P < .0001). Intra- and interobserver correlations for SECM counts were very good (R = 0.93 and R = 0.92, respectively; P < .0001). For the commonly used eosinophil count cutoff of 15 per high-power field, the sensitivity and specificity of SECM for EoE were 100%. The sensitivity and specificity for abscess, degranulation, and basal cell hyperplasia were 100% and 82%, 91% and 60%, and 94% and 80%, respectively. Intra- and interobserver agreements for these microscopic features of EoE were very good (κ = 0.9/0.9, 0.84/1.0, 0.91/0.81, respectively).
Limitation: Ex vivo study.
Conclusions: This study demonstrates that RCM can be used to accurately count intraepithelial eosinophils and identify other microscopic abnormalities associated with EoE on freshly excised biopsy samples. These findings suggest that RCM may be developed into a tool for assessing eosinophilic infiltration in the esophagus in vivo.
Copyright © 2011 American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy. Published by Mosby, Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Determination of esophageal eosinophil counts and other histologic features of eosinophilic esophagitis by pathology trainees is highly accurate.Hum Pathol. 2017 Apr;62:50-55. doi: 10.1016/j.humpath.2016.12.017. Epub 2016 Dec 30. Hum Pathol. 2017. PMID: 28041975 Free PMC article.
-
Prospective assessment of the diagnostic utility of esophageal brushings in adults with eosinophilic esophagitis.Dis Esophagus. 2016 Jan;29(1):48-53. doi: 10.1111/dote.12304. Epub 2014 Dec 17. Dis Esophagus. 2016. PMID: 25515533
-
Comprehensive imaging of gastroesophageal biopsy samples by spectrally encoded confocal microscopy.Gastrointest Endosc. 2010 Jan;71(1):35-43. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2009.08.026. Epub 2009 Nov 17. Gastrointest Endosc. 2010. PMID: 19922916 Free PMC article.
-
[Eosinophilic esophagitis: the diagnostic contribution of pathology].Pathologe. 2013 Mar;34(2):110-7. doi: 10.1007/s00292-012-1721-6. Pathologe. 2013. PMID: 23483314 Review. German.
-
Eosinophilic esophagitis.Allergy Asthma Proc. 2019 Nov 1;40(6):462-464. doi: 10.2500/aap.2019.40.4272. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2019. PMID: 31690395 Review.
Cited by
-
Optical endomicroscopy and the road to real-time, in vivo pathology: present and future.Diagn Pathol. 2012 Aug 13;7:98. doi: 10.1186/1746-1596-7-98. Diagn Pathol. 2012. PMID: 22889003 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Eosinophilic esophagitis: diagnostic tests and criteria.Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 2012 Jul;28(4):382-8. doi: 10.1097/MOG.0b013e328352b5ef. Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 2012. PMID: 22450900 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multimodal microscopy for the simultaneous visualization of five different imaging modalities using a single light source.Biomed Opt Express. 2021 Aug 9;12(9):5452-5469. doi: 10.1364/BOE.430677. eCollection 2021 Sep 1. Biomed Opt Express. 2021. PMID: 34692194 Free PMC article.
-
A miniaturized, tethered, spectrally-encoded confocal endomicroscopy capsule.Lasers Surg Med. 2019 Jul;51(5):452-458. doi: 10.1002/lsm.23050. Epub 2019 Jan 6. Lasers Surg Med. 2019. PMID: 30614021 Free PMC article.
-
Transnasal Endoscopy in Unsedated Children With Eosinophilic Esophagitis Using Virtual Reality Video Goggles.Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019 Nov;17(12):2455-2462. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2019.01.023. Epub 2019 Jan 29. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019. PMID: 30708107 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chehade M, Sampson HA. Epidemiology and etiology of eosinophilc esophagitis. Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am. 2008;18:33–44. viii. - PubMed
-
- Kapel RC, Miller JK, Torres C, et al. Eosinophilic esophagitis: a prevalent disease in the United States that affects all age groups. Gastroenterology. 2008;134:1316–21. - PubMed
-
- Veerappan GR, Perry JL, Duncan TJ, et al. Prevalence of eosinophilic esophagitis in an adult population undergoing upper endoscopy: a prospective study. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2009;7:420–6. 426, e1–2. - PubMed
-
- Liacouras CA. Eosinophilic esophagitis. Gastroenterol Clin North Am. 2008;37:989–98. xi. - PubMed
-
- Atkins D, Kramer R, Capocelli K, et al. Eosinophilic esophagitis: the newest esophageal inflammatory disease. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2009;6:267–78. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

