Drug repositioning and pharmacophore identification in the discovery of hookworm MIF inhibitors
- PMID: 21944748
- PMCID: PMC3294498
- DOI: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2011.07.011
Drug repositioning and pharmacophore identification in the discovery of hookworm MIF inhibitors
Abstract
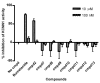
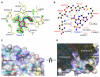
The screening of bioactive compound libraries can be an effective approach for repositioning FDA-approved drugs or discovering new pharmacophores. Hookworms are blood-feeding, intestinal nematode parasites that infect up to 600 million people worldwide. Vaccination with recombinant Ancylostoma ceylanicum macrophage migration inhibitory factor (rAceMIF) provided partial protection from disease, thus establishing a "proof-of-concept" for targeting AceMIF to prevent or treat infection. A high-throughput screen (HTS) against rAceMIF identified six AceMIF-specific inhibitors. A nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID), sodium meclofenamate, could be tested in an animal model to assess the therapeutic efficacy in treating hookworm disease. Furosemide, an FDA-approved diuretic, exhibited submicromolar inhibition of rAceMIF tautomerase activity. Structure-activity relationships of a pharmacophore based on furosemide included one analog that binds similarly to the active site, yet does not inhibit the Na-K-Cl symporter (NKCC1) responsible for diuretic activity.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures



References
-
- Al-Abed Y, Dabideen D, Aljabari B, Valster A, Messmer D, Ochani M, Tanovic M, Ochani K, Bacher M, Nicoletti F, et al. ISO-1 binding to the tautomerase active site of MIF inhibits its pro-inflammatory activity and increases survival in severe sepsis. J. Biol. Chem. 2005;280:36541–36544. - PubMed
-
- Albonico M, Engels D, Savioli L. Monitoring drug efficacy and early detection of drug resistance in human soil-transmitted nematodes: a pressing public health agenda for helminth control. Int. J. Parasitol. 2004;34:1205–1210. - PubMed
-
- Bernhagen J, Krohn R, Lue H, Gregory JL, Zernecke A, Koenen RR, Dewor M, Georgiev I, Schober A, Leng L, et al. MIF is a noncognate ligand of CXC chemokine receptors in inflammatory and atherogenic cell recruitment. Nat. Med. 2007;13:587–596. - PubMed
-
- Bethony J, Brooker S, Albonico M, Geiger SM, Loukas A, Diemert D, Hotez PJ. Soil-transmitted helminth infections: ascariasis, trichuriasis, and hookworm. Lancet. 2006;367:1521–1532. - PubMed
-
- Bungiro R, Cappello M. Hookworm infection: new developments and prospects for control. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2004;17:421–426. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

