A hexanucleotide repeat expansion in C9ORF72 is the cause of chromosome 9p21-linked ALS-FTD
- PMID: 21944779
- PMCID: PMC3200438
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2011.09.010
A hexanucleotide repeat expansion in C9ORF72 is the cause of chromosome 9p21-linked ALS-FTD
Abstract
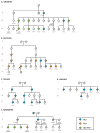
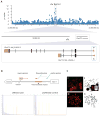
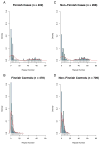
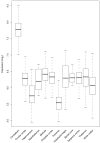
The chromosome 9p21 amyotrophic lateral sclerosis-frontotemporal dementia (ALS-FTD) locus contains one of the last major unidentified autosomal-dominant genes underlying these common neurodegenerative diseases. We have previously shown that a founder haplotype, covering the MOBKL2b, IFNK, and C9ORF72 genes, is present in the majority of cases linked to this region. Here we show that there is a large hexanucleotide (GGGGCC) repeat expansion in the first intron of C9ORF72 on the affected haplotype. This repeat expansion segregates perfectly with disease in the Finnish population, underlying 46.0% of familial ALS and 21.1% of sporadic ALS in that population. Taken together with the D90A SOD1 mutation, 87% of familial ALS in Finland is now explained by a simple monogenic cause. The repeat expansion is also present in one-third of familial ALS cases of outbred European descent, making it the most common genetic cause of these fatal neurodegenerative diseases identified to date.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Comment in
-
A hexanucleotide repeat expansion in C9ORF72 links amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and frontotemporal dementia.Nat Rev Neurol. 2011 Oct 18;7(11):595. doi: 10.1038/nrneurol.2011.162. Nat Rev Neurol. 2011. PMID: 22009283 No abstract available.
-
FTD and ALS: genetic ties that bind.Neuron. 2011 Oct 20;72(2):189-90. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2011.10.001. Neuron. 2011. PMID: 22017980
-
A nasty hex on chromosome 9 causes FTD/ALS.Clin Genet. 2012 Feb;81(2):126-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.2011.01820.x. Epub 2011 Dec 28. Clin Genet. 2012. PMID: 22129088 No abstract available.
-
New gene for ALS–FTD.Mov Disord. 2012 Feb;27(2):202. doi: 10.1002/mds.24904. Mov Disord. 2012. PMID: 22423382 No abstract available.
References
-
- Cann HM, de Toma C, Cazes L, Legrand MF, Morel V, Piouffre L, Bodmer J, Bodmer WF, Bonne-Tamir B, Cambon-Thomsen A, et al. A human genome diversity cell line panel. Science. 2002;296:261–262. - PubMed
-
- Chiò A, Traynor BJ, Lombardo F, Fimognari M, Calvo A, Ghiglione P, Mutani R, Restagno G. Prevalence of SOD1 mutations in the Italian ALS population. Neurology. 2008;70:533–537. - PubMed
-
- DeBose-Boyd RA, Brown MS, Li WP, Nohturfft A, Goldstein JL, Espenshade PJ. Transport-dependent proteolysis of SREBP: relocation of site-1 protease from Golgi to ER obviates the need for SREBP transport to Golgi. Cell. 1999;99:703–712. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- 089701/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- G0802462/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- Z01 AG000949/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- U24 AG021886/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- MC_G0901330/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G0701075/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_G1000735/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- 089703/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- 089698/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- G0701441/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- Z01-AG000949-02/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- G0700943/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_G1000734/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_PC_09003/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- ZIA AG000933/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

