High expression of BMP pathway genes distinguishes a subset of atypical teratoid/rhabdoid tumors associated with shorter survival
- PMID: 21946044
- PMCID: PMC3223096
- DOI: 10.1093/neuonc/nor140
High expression of BMP pathway genes distinguishes a subset of atypical teratoid/rhabdoid tumors associated with shorter survival
Abstract
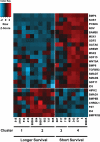
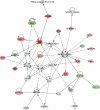
Molecular profiling of tumors has proven to be a valuable tool for identification of prognostic and diagnostic subgroups in medulloblastomas, glioblastomas, and other cancers. However, the molecular landscape of atypical teratoid/rhabdoid tumors (AT/RTs) remains largely unexplored. To address this issue, we used microarrays to measure the gene expression profiles of 18 AT/RTs and performed unsupervised hierarchical clustering to determine molecularly similar subgroups. Four major subgroups (clusters) were identified. These did not conform to sex, tumor location, or presence of monosomy 22. Clusters showed distinct gene signatures and differences in enriched biological processes, including elevated expression of some genes associated with choroid plexus lineage in cluster 4. In addition, survival differed significantly by cluster, with shortest survival (mean, 4.7 months) in both clusters 3 and 4, compared with clusters 1 and 2 (mean, 28.1 months). Analysis showed that multiple bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) pathway genes were upregulated in the short survival clusters, with BMP4 showing the most significant upregulation (270-fold). Thus, high expression of BMP pathway genes was negatively associated with survival in this dataset. Our study indicates that molecular subgroups exist in AT/RTs and that molecular profiling of these comparatively rare tumors may be of diagnostic, prognostic, and therapeutic value.
Figures



References
-
- Louis DN. International Agency for Research on Cancer. World Health Organization. WHO classification of tumours of the central nervous system. 4th ed. Lyon: International Agency for Research on Cancer; 2007.
-
- Biegel JA, Tan L, Zhang F, Wainwright L, Russo P, Rorke LB. Alterations of the hSNF5/INI1 gene in central nervous system atypical teratoid/rhabdoid tumors and renal and extrarenal rhabdoid tumors. Clin. Cancer Res. 2002;8(11):3461–3467. - PubMed
-
- Judkins AR, Mauger J, Ht A, Rorke LB, Biegel JA. Immunohistochemical analysis of hSNF5/INI1 in pediatric CNS neoplasms. Am J Surg Pathol. 2004;28(5):644–650. doi:10.1097/00000478-200405000-00013. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Hilden JM, Meerbaum S, Burger P, et al. Central nervous system atypical teratoid/rhabdoid tumor: results of therapy in children enrolled in a registry. J Clin Oncol. 2004;22(14):2877–2884. doi:10.1200/JCO.2004.07.073. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Chen ML, McComb JG, Krieger MD. Atypical teratoid/rhabdoid tumors of the central nervous system: management and outcomes. Neurosurg Focus. 2005;18(6A):E8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

