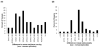Immediate antecedents of marijuana use: an analysis from ecological momentary assessment
- PMID: 21946296
- PMCID: PMC3241527
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jbtep.2011.09.010
Immediate antecedents of marijuana use: an analysis from ecological momentary assessment
Abstract
Background and objectives: Marijuana remains the most commonly used illicit substance. Marijuana craving, anxiety, and peer marijuana use are thought to play important roles in the etiology and maintenance of marijuana use. The present study aimed to identify patterns between marijuana use and these affective and situational risk factors in the natural environment.
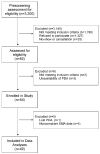
Methods: The sample consisted of 49 current marijuana users (38.8% female), 63.2% of whom evinced a current cannabis use disorder. Ecological momentary assessment was used to collect multiple daily ratings of marijuana craving, state anxiety, and peer marijuana use over two weeks. Mixed effects linear models were used to examine within- and between-day antecedents, correlates, and consequences of marijuana use.
Results: Between-day analyses indicated that marijuana use days were associated with higher marijuana craving but lower state anxiety. Within-day analyses confirmed that marijuana craving was higher prior to marijuana use and lower following use. Anxiety was related to marijuana craving. Although anxiety was somewhat higher prior to marijuana use, it did not decrease significantly following use. The vast majority of marijuana use occurred when others were also using marijuana.
Limitations: The sample was comprised of college students, a group at particular risk for marijuana use and use-related problems. Future work is necessary to determine whether results generalize to other populations.
Conclusions: These data support the contention that marijuana craving, anxiety, and peer use play important roles in the maintenance of marijuana use.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures