Genome-wide association and large-scale follow up identifies 16 new loci influencing lung function
- PMID: 21946350
- PMCID: PMC3267376
- DOI: 10.1038/ng.941
Genome-wide association and large-scale follow up identifies 16 new loci influencing lung function
Abstract
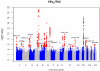
Pulmonary function measures reflect respiratory health and are used in the diagnosis of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. We tested genome-wide association with forced expiratory volume in 1 second and the ratio of forced expiratory volume in 1 second to forced vital capacity in 48,201 individuals of European ancestry with follow up of the top associations in up to an additional 46,411 individuals. We identified new regions showing association (combined P < 5 × 10(-8)) with pulmonary function in or near MFAP2, TGFB2, HDAC4, RARB, MECOM (also known as EVI1), SPATA9, ARMC2, NCR3, ZKSCAN3, CDC123, C10orf11, LRP1, CCDC38, MMP15, CFDP1 and KCNE2. Identification of these 16 new loci may provide insight into the molecular mechanisms regulating pulmonary function and into molecular targets for future therapy to alleviate reduced lung function.
Figures


References
-
- Wilk JB, et al. Evidence for major genes influencing pulmonary function in the NHLBI family heart study. Genet Epidemiol. 2000;19:81–94. - PubMed
-
- Young RP, Hopkins R, Eaton TE. Forced expiratory volume in one second: not just a lung function test but a marker of premature death from all causes. Eur Respir J. 2007;30:616–22. - PubMed
-
- Lopez AD, et al. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: current burden and future projections. Eur Respir J. 2006;27:397–412. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- M01-RR00425/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100012C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1RR025005/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- 079895/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- R01 ES015794/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- N02-HL-6-4278/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- CZB/4/710/CSO_/Chief Scientist Office/United Kingdom
- N01 HC045204/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- CA55769/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095095/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100009I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-45205/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH063706/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- CZD/16/6/2/CSO_/Chief Scientist Office/United Kingdom
- N01-HC-95162/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- G0801056/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G0401540/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- U19 CA148127/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL-071022/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- MC_UP_A620_1015/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- N01-HC-05187/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 268201100011C/PHS HHS/United States
- N01 AG012100/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL071251/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC048048/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC-25195/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 268201100005C/PHS HHS/United States
- BB/F019394/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- MOP-82893/CAPMC/ CIHR/Canada
- HHSN268201100010C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-85085/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01HL59367/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR025005/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- 268201100007C/PHS HHS/United States
- R01 AG015928/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- ES015794/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- N01 AG062101/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100008C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL080295/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL087679/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL-074104/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL071259/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-48047/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095169/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100005G/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL074104/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100008I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA121197/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL071252/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-85081/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL059367/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 068545/Z/02/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- HHSN268201100007C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL105756/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 268200782096C/PHS HHS/United States
- RR-024156/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- MC_U127561128/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- N01-HC-95163/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC015103/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-95168/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 092731/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- GR069224/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- N01 HC085086/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- CZD/16/6/CSO_/Chief Scientist Office/United Kingdom
- CA127219/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R56 AG020098/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL077612/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 268201100008C/PHS HHS/United States
- 5R01MH63706:02/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100011I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 268201100012C/PHS HHS/United States
- MC_U123092721/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- HHSN268201100011C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC048049/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- DH_/Department of Health/United Kingdom
- UL1 RR024156/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- RC1 AG035835/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-45204/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL071250/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL086694/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA127219/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-95159/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 1R01AG032098-01A1/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- RG/08/013/25942/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- RC1 HL100543/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 1RL1MH083268-01/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL087652/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- AG-20098/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-95095/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG004402/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-95165/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL087652/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 AG062106/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01-HL-084099/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01HL071252/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-85086/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095159/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- AG-027058/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- MC_UP_A620_1014/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 AG032098/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-48050/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL105756/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC045205/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01HL071205/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- AG035835/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- G1000861/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G9901462/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- N01-HC-85082/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01CA111703/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK062418/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG004729/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- AG-023269/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- 268200625226C/PHS HHS/United States
- HHSN268200782096C/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100006C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC-55222/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- PG/06/154/22043/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- P30 DK063491/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL071051/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- MC_U123092720/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 CA055769/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC025195/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01HL087641/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 268201100009C/PHS HHS/United States
- N01 HC055222/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-95169/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100005I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 AG062103/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-95164/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL071022/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- G0800582/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G0701863/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 HL-077612/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-48049/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-85083/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL084099/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC045134/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-85080/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 077016/Z/05/Z/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- 1P50 CA70907/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC005187/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC085079/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 090532/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- N01-HC-75150/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-95160/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- CZD/16/6/4/CSO_/Chief Scientist Office/United Kingdom
- MC_PC_U127561128/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01-HL084099/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- G20234/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- FS05/125/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- R01 HL080295/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC048047/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL075336/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL075476/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000425/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- G0500539/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 AG020098/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01-HG-004729/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- G0000934/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- P50 CA070907/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100005C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 268201100006C/PHS HHS/United States
- R01 HL071205/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100009C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC048050/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- G0902125/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- DK063491/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- 268201100010C/PHS HHS/United States
- M01 RR000997/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100007I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-85079/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-95161/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL080295/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 5R01HL087679-02/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- G0501942/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01HL071259/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- RL1 MH083268/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- G0902313/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- N01-HC-48048/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01HL071251/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC075150/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-95166/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL087641/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01-HG-004402/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- 1K23HL094531-01/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K23 HL094531/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01HL071258/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG027058/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- MC_U106188470/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- N01 HC045133/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL088133/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01HL071051/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 5M01 RR00997/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL071258/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- Z01 ES049019/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC035129/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01HL071250/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- ZO1 ES49019/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- N01-HC-85084/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 076113/B/04/Z/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- HL088133/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA111703/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- G9815508/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- N01-HC-95167/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01HL086694/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- PG/97012/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- G0600705/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

