Sustained-release delivery of octreotide from biodegradable polymeric microspheres
- PMID: 21948321
- PMCID: PMC3225556
- DOI: 10.1208/s12249-011-9693-z
Sustained-release delivery of octreotide from biodegradable polymeric microspheres
Abstract
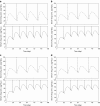
The study reports on the drug release behavior of a potent synthetic somatostatin analogue, octreotide acetate, from biocompatible and biodegradable microspheres composed of poly-lactic-co-glycolic acid (PLGA) following a single intramuscular depot injection. The serum octreotide levels of three Oakwood Laboratories formulations and one Sandostatin LAR(®) formulation were compared. Three formulations of octreotide acetate-loaded PLGA microspheres were prepared by a solvent extraction and evaporation procedure using PLGA polymers with different molecular weights. The in vivo drug release study was conducted in male Sprague-Dawley rats. Blood samples were taken at predetermined time points for up to 70 days. Drug serum concentrations were quantified using a radioimmunoassay procedure consisting of radiolabeled octreotide. The three octreotide PLGA microsphere formulations and Sandostatin LAR(®) all showed a two-phase drug release profile (i.e., bimodal). The peak serum drug concentration of octreotide was reached in 30 min for all formulations followed by a decline after 6 h. Following this initial burst and decline, a second-release phase occurred after 3 days. This second-release phase exhibited sustained-release behavior, as the drug serum levels were discernible between days 7 and 42. Using pharmacokinetic computer simulations, it was estimated that the steady-state octreotide serum drug levels would be predicted to fall in the range of 40-130 pg/10 μL and 20-100 pg/10 μL following repeat dosing of the Oakwood formulations and Sandostatin LAR(®) every 28 days and every 42 days at a dose of 3 mg/rat, respectively.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

