Rasch analysis of the Ocular Surface Disease Index (OSDI)
- PMID: 21948646
- PMCID: PMC3230285
- DOI: 10.1167/iovs.11-8027
Rasch analysis of the Ocular Surface Disease Index (OSDI)
Abstract
Purpose: The Ocular Surface Disease Index (OSDI) is a 12-item scale for the assessment of symptoms related to dry eye disease and their effect on vision. Its reliability and validity have been investigated within the classical test theory framework and, more recently, using Rasch analysis. The purpose of the present analysis was to more completely investigate the functioning of its response category structure, the validity of its three subscales, and the unidimensionality of the latent construct it is intended to assess.
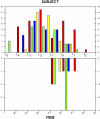
Methods: Responses to the OSDI from 172 females participating in the Dry Eye in Postmenopause (DEiM) study who had previously been diagnosed with dry eye or reported significant ocular irritation and dryness were analyzed. Response category structure and item fit statistics were evaluated for assessment of model fit. Person separation statistics were used to examine the validity of the subscales. Unidimensionality was assessed by principal component analysis (PCA) of model residuals.
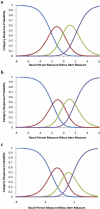
Results: The recommended five-category response structure resulted in disordered response thresholds. A four-category structure resulted in ordered thresholds. Item infit statistics were acceptable for all 12 items. Person separation with this category structure was adequate, with a person separation index of 2.16. None of the three subscales demonstrated adequate person separation. PCA showed one other significant factor onto which the three environmental items loaded significantly.
Conclusions: All items demonstrated acceptable fit to the model after collapsing categories to order the response thresholds. The original subscales did not prove valid, and there is some evidence of multidimensionality and poor targeting.
Figures

References
-
- Gurdal C, Sarac O, Genc I, Kirimlioglu H, Takmaz T, Can I. Ocular surface and dry eye in Graves' disease. Curr Eye Res. 2011;36:8–13 - PubMed
-
- Rossi GC, Tinelli C, Pasinetti GM, Milano G, Bianchi PE. Dry eye syndrome-related quality of life in glaucoma patients. Eur J Ophthalmol. 2009;19:572–579 - PubMed
-
- Adatia FA, Michaeli-Cohen A, Naor J, Caffery B, Bookman A, Slomovic A. Correlation between corneal sensitivity, subjective dry eye symptoms and corneal staining in Sjogren's syndrome. Can J Ophthalmol. 2004;39:767–771 - PubMed
-
- Monaco G, Cacioppo V, Consonni D, Troiano P. Effects of osmoprotection on symptoms, ocular surface damage, and tear film modifications caused by glaucoma therapy. Eur J Ophthalmol. 2011;21:243–250 - PubMed
-
- Luchs JI, Nelinson DS, Macy JI. Efficacy of hydroxypropyl cellulose ophthalmic inserts (LACRISERT) in subsets of patients with dry eye syndrome: findings from a patient registry. Cornea. 2010;29:1417–1427 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

