Identification of essential subunits in the plastid-encoded RNA polymerase complex reveals building blocks for proper plastid development
- PMID: 21949211
- PMCID: PMC3252157
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.111.184515
Identification of essential subunits in the plastid-encoded RNA polymerase complex reveals building blocks for proper plastid development
Abstract
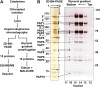
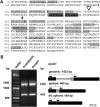
The major RNA polymerase activity in mature chloroplasts is a multisubunit, Escherichia coli-like protein complex called PEP (for plastid-encoded RNA polymerase). Its subunit structure has been extensively investigated by biochemical means. Beside the "prokaryotic" subunits encoded by the plastome-located RNA polymerase genes, a number of additional nucleus-encoded subunits of eukaryotic origin have been identified in the PEP complex. These subunits appear to provide additional functions and regulation modes necessary to adapt transcription to the varying functional situations in chloroplasts. However, despite the enormous progress in genomic data and mass spectrometry techniques, it is still under debate which of these subunits belong to the core complex of PEP and which ones represent rather transient or peripheral components. Here, we present a catalog of true PEP subunits that is based on comparative analyses from biochemical purifications, protein mass spectrometry, and phenotypic analyses. We regard reproducibly identified protein subunits of the basic PEP complex as essential when the corresponding knockout mutants reveal an albino or pale-green phenotype. Our study provides a clearly defined subunit catalog of the basic PEP complex, generating the basis for a better understanding of chloroplast transcription regulation. In addition, the data support a model that links PEP complex assembly and chloroplast buildup during early seedling development in vascular plants.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Structure of the plant plastid-encoded RNA polymerase.Cell. 2024 Feb 29;187(5):1145-1159.e21. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2024.01.036. Cell. 2024. PMID: 38428394
-
Plastid Deficient 1 Is Essential for the Accumulation of Plastid-Encoded RNA Polymerase Core Subunit β and Chloroplast Development in Arabidopsis.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Dec 20;22(24):13648. doi: 10.3390/ijms222413648. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34948448 Free PMC article.
-
Transcription of plastid genes is modulated by two nuclear-encoded alpha subunits of plastid RNA polymerase in the moss Physcomitrella patens.Plant J. 2007 Nov;52(4):730-41. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2007.03270.x. Epub 2007 Sep 25. Plant J. 2007. PMID: 17894784
-
[Plastid RNA polymerases].Mol Biol (Mosk). 2005 Sep-Oct;39(5):762-75. Mol Biol (Mosk). 2005. PMID: 16240710 Review. Russian.
-
The plastid transcription machinery and its coordination with the expression of nuclear genome: Plastid-Encoded Polymerase, Nuclear-Encoded Polymerase and the Genomes Uncoupled 1-mediated retrograde communication.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2020 Jun 22;375(1801):20190399. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2019.0399. Epub 2020 May 4. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32362266 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
How to build functional thylakoid membranes: from plastid transcription to protein complex assembly.Planta. 2013 Feb;237(2):413-28. doi: 10.1007/s00425-012-1752-5. Epub 2012 Sep 14. Planta. 2013. PMID: 22976450 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nucleo-plastidic PAP8/pTAC6 couples chloroplast formation with photomorphogenesis.EMBO J. 2020 Nov 16;39(22):e104941. doi: 10.15252/embj.2020104941. Epub 2020 Oct 1. EMBO J. 2020. PMID: 33001465 Free PMC article.
-
The plastid-localized pfkB-type carbohydrate kinases FRUCTOKINASE-LIKE 1 and 2 are essential for growth and development of Arabidopsis thaliana.BMC Plant Biol. 2012 Jul 8;12:102. doi: 10.1186/1471-2229-12-102. BMC Plant Biol. 2012. PMID: 22770232 Free PMC article.
-
Regulatory role of Arabidopsis pTAC14 in chloroplast development and plastid gene expression.Plant Signal Behav. 2012 Oct 1;7(10):1354-6. doi: 10.4161/psb.21618. Epub 2012 Aug 20. Plant Signal Behav. 2012. PMID: 22902688 Free PMC article.
-
GUN1, a Jack-Of-All-Trades in Chloroplast Protein Homeostasis and Signaling.Front Plant Sci. 2016 Sep 22;7:1427. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2016.01427. eCollection 2016. Front Plant Sci. 2016. PMID: 27713755 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abdallah F, Salamini F, Leister D. (2000) A prediction of the size and evolutionary origin of the proteome of chloroplasts of Arabidopsis. Trends Plant Sci 5: 141–142 - PubMed
-
- Allison LA. (2000) The role of sigma factors in plastid transcription. Biochimie 82: 537–548 - PubMed
-
- Arsova B, Hoja U, Wimmelbacher M, Greiner E, Ustün S, Melzer M, Petersen K, Lein W, Börnke F. (2010) Plastidial thioredoxin z interacts with two fructokinase-like proteins in a thiol-dependent manner: evidence for an essential role in chloroplast development in Arabidopsis and Nicotiana benthamiana. Plant Cell 22: 1498–1515 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

