Metformin in gestational diabetes: the offspring follow-up (MiG TOFU): body composition at 2 years of age
- PMID: 21949222
- PMCID: PMC3177748
- DOI: 10.2337/dc11-0660
Metformin in gestational diabetes: the offspring follow-up (MiG TOFU): body composition at 2 years of age
Abstract
Objective: In women with gestational diabetes mellitus, who were randomized to metformin or insulin treatment, pregnancy outcomes were similar (Metformin in Gestational diabetes [MiG] trial). Metformin crosses the placenta, so it is important to assess potential effects on growth of the children.
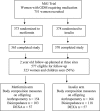
Research design and methods: In Auckland, New Zealand, and Adelaide, Australia, women who had participated in the MiG trial were reviewed when their children were 2 years old. Body composition was measured in 154 and 164 children whose mothers had been randomized to metformin and insulin, respectively. Children were assessed with anthropometry, bioimpedance, and dual energy X-ray absorptiometry (DEXA), using standard methods.
Results: The children were similar for baseline maternal characteristics and pregnancy outcomes. In the metformin group, compared with the insulin group, children had larger mid-upper arm circumferences (17.2 ± 1.5 vs. 16.7 ± 1.5 cm; P = 0.002) and subscapular (6.3 ± 1.9 vs. 6.0 ± 1.7 mm; P = 0.02) and biceps skinfolds (6.03 ± 1.9 vs. 5.6 ± 1.7 mm; P = 0.04). Total fat mass and percentage body fat assessed by bioimpedance (n = 221) and DEXA (n = 114) were not different.
Conclusions: Children exposed to metformin had larger measures of subcutaneous fat, but overall body fat was the same as in children whose mothers were treated with insulin alone. Further follow-up is required to examine whether these findings persist into later life and whether children exposed to metformin will develop less visceral fat and be more insulin sensitive. If so, this would have significant implications for the current pandemic of diabetes.
Figures
Comment in
-
Metformin therapy during pregnancy: good for the goose and good for the gosling too?Diabetes Care. 2011 Oct;34(10):2329-30. doi: 10.2337/dc11-1153. Diabetes Care. 2011. PMID: 21949224 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Comment on: Rowan et al. Metformin in Gestational diabetes: The Offspring Follow-Up (MiG TOFU): body composition at 2 years of age. Diabetes Care 2011;34:2279-2284.Diabetes Care. 2012 Mar;35(3):e28; author reply e30. doi: 10.2337/dc11-2107. Diabetes Care. 2012. PMID: 22355031 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Comment on: Rowan et al. Metformin in Gestational diabetes: The Offspring Follow-Up (MiG TOFU): body composition at 2 years of age. Diabetes Care 2011;34:2279-2284.Diabetes Care. 2012 Mar;35(3):e29; author reply e30. doi: 10.2337/dc11-2241. Diabetes Care. 2012. PMID: 22355032 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Rowan JA, Hague WM, Gao W, Battin MR, Moore MP; MiG Trial Investigators Metformin versus insulin for the treatment of gestational diabetes. N Engl J Med 2008;358:2003–2015 - PubMed
-
- Charles B, Norris R, Xiao X, Hague W. Population pharmacokinetics of metformin in late pregnancy. Ther Drug Monit 2006;28:67–72 - PubMed
-
- Catalano PM, Thomas A, Huston-Presley L, Amini SB. Increased fetal adiposity: a very sensitive marker of abnormal in utero development. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2003;189:1698–1704 - PubMed
-
- Ali AT, Ferris WF, Naran NH, Crowther NJ. Insulin resistance in the control of body fat distribution: a new hypothesis. Horm Metab Res 2011;43:77–80 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials