Sir-two-homolog 2 (Sirt2) modulates peripheral myelination through polarity protein Par-3/atypical protein kinase C (aPKC) signaling
- PMID: 21949390
- PMCID: PMC3203793
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1104969108
Sir-two-homolog 2 (Sirt2) modulates peripheral myelination through polarity protein Par-3/atypical protein kinase C (aPKC) signaling
Abstract
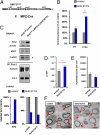
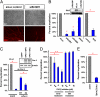
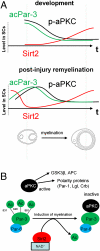
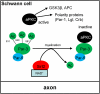
The formation of myelin by Schwann cells (SCs) occurs via a series of orchestrated molecular events. We previously used global expression profiling to examine peripheral nerve myelination and identified the NAD(+)-dependent deacetylase Sir-two-homolog 2 (Sirt2) as a protein likely to be involved in myelination. Here, we show that Sirt2 expression in SCs is correlated with that of structural myelin components during both developmental myelination and remyelination after nerve injury. Transgenic mice lacking or overexpressing Sirt2 specifically in SCs show delays in myelin formation. In SCs, we found that Sirt2 deacetylates Par-3, a master regulator of cell polarity. The deacetylation of Par-3 by Sirt2 decreases the activity of the polarity complex signaling component aPKC, thereby regulating myelin formation. These results demonstrate that Sirt2 controls an essential polarity pathway in SCs during myelin assembly and provide insights into the association between intracellular metabolism and SC plasticity.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: The authors and Washington University may derive benefit from a licensing agreement with Sirtris Pharmaceuticals, which did not provide any support for this work.
Figures



References
-
- Nave KA. Myelination and support of axonal integrity by glia. Nature. 2010;468:244–252. - PubMed
-
- Fawcett JW, Keynes RJ. Peripheral nerve regeneration. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1990;13:43–60. - PubMed
-
- Le N, et al. Nab proteins are essential for peripheral nervous system myelination. Nat Neurosci. 2005;8:932–940. - PubMed
-
- Ekström AR, Tomlinson DR. Impaired nerve regeneration in streptozotocin-diabetic rats. Effects of treatment with an aldose reductase inhibitor. J Neurol Sci. 1989;93:231–237. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- AG13730/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 NS057105/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS040745/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK019645/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K08 NS055980/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- RF1 AG013730/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 DK059820/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- 231138/ERC_/European Research Council/International
- P01 AG027916/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R21NS059566/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- NS055980/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- NS040745/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R56 AG013730/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R37 DK019645/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG013730/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG028730/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- AG027916/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- DK19645/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R37 AG028730/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- DK59820/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R21 NS059566/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG019719/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- AG028730/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

