Structure and function of the skeletal muscle extracellular matrix
- PMID: 21949456
- PMCID: PMC3177172
- DOI: 10.1002/mus.22094
Structure and function of the skeletal muscle extracellular matrix
Abstract
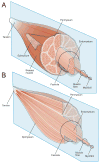
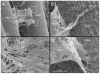
The skeletal muscle extracellular matrix (ECM) plays an important role in muscle fiber force transmission, maintenance, and repair. In both injured and diseased states, ECM adapts dramatically, a property that has clinical manifestations and alters muscle function. Here we review the structure, composition, and mechanical properties of skeletal muscle ECM; describe the cells that contribute to the maintenance of the ECM; and, finally, overview changes that occur with pathology. New scanning electron micrographs of ECM structure are also presented with hypotheses about ECM structure–function relationships. Detailed structure–function relationships of the ECM have yet to be defined and, as a result, we propose areas for future study.
Keywords: Skeletal muscle; biomechanics; collagen; extracellular matrix; fibrosis.
Figures







References
-
- Eisenberg BR. Quantitative ultrastructure of mammalian skeletal muscle. In: Peachey LD, Adrian RH, Geiger SR, editors. Skeletal Muscle. Baltimore, MD: American Physiological Society; 1983. pp. 73–112.
-
- Trotter JA, Purslow PP. Functional morphology of the endomysium in series fibered muscles. J Morphol. 1992;212:109–122. - PubMed
-
- Purslow PP, Trotter JA. The morphology and mechanical properties of endomysium in series-fibred muscles: variations with muscle length. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 1994;15:299–308. - PubMed
-
- Jarvinen TA, Jozsa L, Kannus P, Jarvinen TL, Jarvinen M. Organization and distribution of intramuscular connective tissue in normal and immobilized skeletal muscles. An immunohistochemical, polarization and scanning electron microscopic study. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 2002;23:245–254. - PubMed
-
- Borg TK, Caulfield JB. Morphology of connective tissue in skeletal muscle. Tissue Cell. 1980;12:197–207. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

