Elucidation of the Molecular Mechanisms of Action of the Natural Antimicrobial Peptide Subtilosin Against the Bacterial Vaginosis-associated Pathogen Gardnerella vaginalis
- PMID: 21949544
- PMCID: PMC3176456
- DOI: 10.1007/s12602-010-9061-4
Elucidation of the Molecular Mechanisms of Action of the Natural Antimicrobial Peptide Subtilosin Against the Bacterial Vaginosis-associated Pathogen Gardnerella vaginalis
Abstract
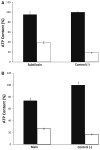
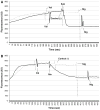
Subtilosin A is a 35-amino acid long cyclical peptide produced by Bacillus amyloliquefaciens that has potent antimicrobial activity against a variety of human pathogens, including the bacterial vaginosis-related Gardnerella vaginalis. The specific mode of action of subtilosin against G. vaginalis was elucidated by studying its effects on the proton motive force's (PMF) components: transmembrane electric potential (ΔΨ), transmembrane pH gradient (ΔpH), and intracellular ATP levels. The addition of subtilosin to G. vaginalis cells caused an immediate and total depletion of the ΔpH, but had no effect on the ΔΨ. Subtilosin also triggered an instant but partial efflux of intracellular ATP that was twofold higher than that of the positive control bacteriocin, nisin. Taken together, these data suggest that subtilosin inhibits G. vaginalis growth by creating transient pores in the cells' cytoplasmic membrane, leading to an efflux of intracellular ions and ATP and eventually cell death.
Figures

References
-
- Amsel R, Totten PA, Spiegel CA, Chen KC, Eschenbach D, Holmes KK. Nonspecific vaginitis. Diagnostic criteria and microbial and epidemiologic associations. Am J Med. 1983;74:14–22. - PubMed
-
- Babasaki K, Takao T, Shimonishi Y, Kurahashi K. Subtilosin A, a new antibiotic peptide produced by Bacillus subtilis 168: isolation, structural analysis, and biogenesis. J Biochem. 1985;98:585–603. - PubMed
-
- Bannatyne RM, Smith AM. Recurrent bacterial vaginosis and metronidazole resistance in Gardnerella vaginalis. Sex Transm Infect. 1998;74:455–456. - PubMed
-
- Bauer R, Chikindas ML, Dicks LMT. Purification, partial amino acid sequence and mode of action of pediocin PD-1, a bacteriocin produced by Pediococcus damnosus NCFB 1832. Int J Food Microbiol. 2005;101:17–27. - PubMed
-
- Chikindas ML, García-Garcerá MJ, Driessen AJ, Ledeboer AM, Nissen-Meyer J, Nes IF, Abee T, Konings WN, Venema G. Pediocin PA-1, a bacteriocin from Pediococcus acidilactici PAC1.0, forms hydrophilic pores in the cytoplasmic membrane of target cells. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1993;59:3577–3584. - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

