Plague and climate: scales matter
- PMID: 21949648
- PMCID: PMC3174245
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1002160
Plague and climate: scales matter
Erratum in
- PLoS Pathog. 2012 May;8(5): doi/10.1371/annotation/84f83f75-2e53-48cf-9f43-7e5eaed74437. Ben Ari, Tamara [corrected to Ben-Ari, Tamara]
Abstract
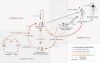
Plague is enzootic in wildlife populations of small mammals in central and eastern Asia, Africa, South and North America, and has been recognized recently as a reemerging threat to humans. Its causative agent Yersinia pestis relies on wild rodent hosts and flea vectors for its maintenance in nature. Climate influences all three components (i.e., bacteria, vectors, and hosts) of the plague system and is a likely factor to explain some of plague's variability from small and regional to large scales. Here, we review effects of climate variables on plague hosts and vectors from individual or population scales to studies on the whole plague system at a large scale. Upscaled versions of small-scale processes are often invoked to explain plague variability in time and space at larger scales, presumably because similar scale-independent mechanisms underlie these relationships. This linearity assumption is discussed in the light of recent research that suggests some of its limitations.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

References
-
- Stenseth NC, Atshabar BB, Begon M, Blemain SR, Bertherat E, et al. Plague: past, present and future. PloS Med. 2008;5:e3. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.0050003. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Catanach IJ. The “globalization” of disease? India and the plague. Journal of World History. 2001;12:131–153. - PubMed
-
- Rogers L. The yearly variations in plague in India in relation to climate: forecasting epidemics. Proc Roy Soc Ser B. 1928;103:42–72.
-
- Cavanaugh DC, Marshall JD. The influence of climate on the seasonal prevalence of plague in the Republic of Vietnam. J Wildl Dis. 1972;8:85–94. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

