Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infection and hospitalization in high-risk patients in the year following detection
- PMID: 21949707
- PMCID: PMC3174953
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0024340
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infection and hospitalization in high-risk patients in the year following detection
Abstract
Background: Many studies have evaluated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) infections during single hospitalizations and subsequent readmissions to the same institution. None have assessed the comprehensive burden of MRSA infection in the period after hospital discharge while accounting for healthcare utilization across institutions.
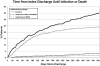
Methodology/principal findings: We conducted a retrospective cohort study of adult patients insured by Harvard Pilgrim Health Care who were newly-detected to harbor MRSA between January 1991 and December 2003 at a tertiary care medical center. We evaluated all MRSA-attributable infections associated with hospitalization in the year following new detection, regardless of hospital location. Data were collected on comorbidities, healthcare utilization, mortality and MRSA outcomes. Of 591 newly-detected MRSA carriers, 23% were colonized and 77% were infected upon detection. In the year following detection, 196 (33%) patients developed 317 discrete and unrelated MRSA infections. The most common infections were pneumonia (34%), soft tissue (27%), and primary bloodstream (18%) infections. Infections occurred a median of 56 days post-detection. Of all infections, 26% involved bacteremia, and 17% caused MRSA-attributable death. During the admission where MRSA was newly-detected, 14% (82/576) developed subsequent infection. Of those surviving to discharge, 24% (114/482) developed post-discharge infections in the year following detection. Half (99/185, 54%) of post-discharge infections caused readmission, and most (104/185, 55%) occurred over 90 days post-discharge.
Conclusions/significance: In high-risk tertiary care patients, newly-detected MRSA carriage confers large risks of infection and substantial attributable mortality in the year following acquisition. Most infections occur post-discharge, and 18% of infections associated with readmission occurred in hospitals other than the one where MRSA was newly-detected. Despite gains in reducing MRSA infections during hospitalization, the risk of MRSA infection among critically and chronically ill carriers persists after discharge and warrants targeted prevention strategies.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Coello R, Glynn JR, Gaspar C, Picazzo JJ, Fereres J. Risk factors for developing clinical infection with methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) amongst hospital patients initially only colonized with MRSA. J Hosp Infect. 1997;37:39–46. - PubMed
-
- Pujol M, Peña C, Pallares R, Ayats J, Ariza J, et al. Risk factors for nosocomial bacteremia due to methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1994;13:96–102. - PubMed
-
- Garrouste-Orgeas M, Timsit JF, Kallel H, Ben Ali A, Dumay MF, et al. Colonization with methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in ICU patients: morbidity, mortality, and glycopeptides use. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 2001;22:687–692. - PubMed
-
- Davis KA, Stewart JJ, Crouch HK, Florez CE, Hospenthal DR. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) nares colonization at hospital admission and its effect on subsequent MRSA infection. Clin Infect Dis. 2004;39:776–782. - PubMed
-
- Keene A, Lemos-Filho L, Levi M, Gomez-Marquez J, Yunen J, et al. The use of a critical care consult team to identify risk for methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infection and the potential for early intervention: A pilot study. Crit Care Med. 2010;38:109–113. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases