Genetics of sputum gene expression in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- PMID: 21949713
- PMCID: PMC3174957
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0024395
Genetics of sputum gene expression in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
Abstract
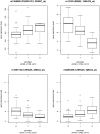
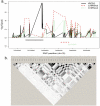
Previous expression quantitative trait loci (eQTL) studies have performed genetic association studies for gene expression, but most of these studies examined lymphoblastoid cell lines from non-diseased individuals. We examined the genetics of gene expression in a relevant disease tissue from chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) patients to identify functional effects of known susceptibility genes and to find novel disease genes. By combining gene expression profiling on induced sputum samples from 131 COPD cases from the ECLIPSE Study with genomewide single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) data, we found 4315 significant cis-eQTL SNP-probe set associations (3309 unique SNPs). The 3309 SNPs were tested for association with COPD in a genomewide association study (GWAS) dataset, which included 2940 COPD cases and 1380 controls. Adjusting for 3309 tests (p<1.5e-5), the two SNPs which were significantly associated with COPD were located in two separate genes in a known COPD locus on chromosome 15: CHRNA5 and IREB2. Detailed analysis of chromosome 15 demonstrated additional eQTLs for IREB2 mapping to that gene. eQTL SNPs for CHRNA5 mapped to multiple linkage disequilibrium (LD) bins. The eQTLs for IREB2 and CHRNA5 were not in LD. Seventy-four additional eQTL SNPs were associated with COPD at p<0.01. These were genotyped in two COPD populations, finding replicated associations with a SNP in PSORS1C1, in the HLA-C region on chromosome 6. Integrative analysis of GWAS and gene expression data from relevant tissue from diseased subjects has located potential functional variants in two known COPD genes and has identified a novel COPD susceptibility locus.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Schadt EE, Monks SA, Drake TA, Lusis AJ, Che N, et al. Genetics of gene expression surveyed in maize, mouse and man. Nature. 2003;422:297–302. - PubMed
-
- Cheung VG, Conlin LK, Weber TM, Arcaro M, Jen KY, et al. Natural variation in human gene expression assessed in lymphoblastoid cells. Nat Genet. 2003;33:422–425. - PubMed
-
- Dixon AL, Liang L, Moffatt MF, Chen W, Heath S, et al. A genome-wide association study of global gene expression. Nat Genet. 2007;39:1202–1207. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- N01 HR076103/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL083069/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HR076102/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HR076114/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01HL084323/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K08HL080242/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HR076101/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01HL094635/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HR076112/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HR076109/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HR076105/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HR076118/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HR076107/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- G0901786/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- K08 HL080242/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- G0901697/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- P01HL083069/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K08 HL097029/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HR076113/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL089897/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL094635/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HR076104/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HR076110/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL089856/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HR076108/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01HL089897/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HR076119/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HR076116/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HR076111/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01HL089856/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HR076115/HR/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL084323/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HR076106/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

