Type III Nrg1 back signaling enhances functional TRPV1 along sensory axons contributing to basal and inflammatory thermal pain sensation
- PMID: 21949864
- PMCID: PMC3176819
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0025108
Type III Nrg1 back signaling enhances functional TRPV1 along sensory axons contributing to basal and inflammatory thermal pain sensation
Abstract
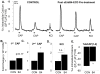
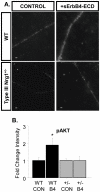
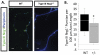
Type III Nrg1, a member of the Nrg1 family of signaling proteins, is expressed in sensory neurons, where it can signal in a bi-directional manner via interactions with the ErbB family of receptor tyrosine kinases (ErbB RTKs). Type III Nrg1 signaling as a receptor (Type III Nrg1 back signaling) can acutely activate phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase (PtdIns3K) signaling, as well as regulate levels of α7* nicotinic acetylcholine receptors, along sensory axons. Transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 (TRPV1) is a cation-permeable ion channel found in primary sensory neurons that is necessary for the detection of thermal pain and for the development of thermal hypersensitivity to pain under inflammatory conditions. Cell surface expression of TRPV1 can be enhanced by activation of PtdIns3K, making it a potential target for regulation by Type III Nrg1. We now show that Type III Nrg1 signaling in sensory neurons affects functional axonal TRPV1 in a PtdIns3K-dependent manner. Furthermore, mice heterozygous for Type III Nrg1 have specific deficits in their ability to respond to noxious thermal stimuli and to develop capsaicin-induced thermal hypersensitivity to pain. Cumulatively, these results implicate Type III Nrg1 as a novel regulator of TRPV1 and a molecular mediator of nociceptive function.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures





References
-
- Caterina MJ, Leffler A, Malmberg AB, Martin WJ, Trafton J, et al. Impaired nociception and pain sensation in mice lacking the capsaicin receptor. Science. 2000;288:306–313. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

