Optical properties of in situ eye lenses measured with X-ray Talbot interferometry: a novel measure of growth processes
- PMID: 21949870
- PMCID: PMC3176817
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0025140
Optical properties of in situ eye lenses measured with X-ray Talbot interferometry: a novel measure of growth processes
Abstract
The lens, a major optical component of the eye, has a gradient refractive index, which is required to provide sufficient refractive power and image quality. The refractive index variations across the lens are dependent on the distributions and concentrations of the varying protein classes. In this study, we present the first measurements of the refractive index in the in situ eye lens from five species using a specially constructed X-ray Talbot grating interferometer. The measurements have been conducted in two planes: the one containing the optic axis (the sagittal plane) and the plane orthogonal to this (the equatorial plane). The results show previously undetected discontinuities and fluctuations in the refractive index profile that vary in different species. These may be linked to growth processes and may be the first optical evidence of discrete developmental stages.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
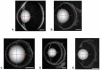

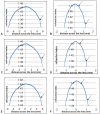


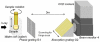
Similar articles
-
Cell compaction is not required for the development of gradient refractive index profiles in the embryonic chick lens.Exp Eye Res. 2020 Aug;197:108112. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2020.108112. Epub 2020 Jun 16. Exp Eye Res. 2020. PMID: 32561482
-
Refractive index degeneration in older lenses: A potential functional correlate to structural changes that underlie cataract formation.Exp Eye Res. 2015 Nov;140:19-27. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2015.08.011. Epub 2015 Aug 18. Exp Eye Res. 2015. PMID: 26297613
-
The eye lens: age-related trends and individual variations in refractive index and shape parameters.Oncotarget. 2015 Oct 13;6(31):30532-44. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.5762. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 26416418 Free PMC article.
-
Optical plasticity in fish lenses.Prog Retin Eye Res. 2013 May;34:78-88. doi: 10.1016/j.preteyeres.2012.12.001. Epub 2012 Dec 20. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2013. PMID: 23262260 Review.
-
The physiological optics of the lens.Prog Retin Eye Res. 2017 Jan;56:e1-e24. doi: 10.1016/j.preteyeres.2016.09.002. Epub 2016 Sep 14. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2017. PMID: 27639549 Review.
Cited by
-
The Connexin50D47A Mutant Causes Cataracts by Calcium Precipitation.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2019 May 1;60(6):2336-2346. doi: 10.1167/iovs.18-26459. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2019. PMID: 31117126 Free PMC article.
-
Solution properties of γ-crystallins: compact structure and low frictional ratio are conserved properties of diverse γ-crystallins.Protein Sci. 2014 Jan;23(1):76-87. doi: 10.1002/pro.2395. Epub 2013 Nov 28. Protein Sci. 2014. PMID: 24214907 Free PMC article.
-
Synchrotron Radiation-based X-ray phase-contrast imaging of the aortic walls in acute aortic dissection.JVS Vasc Sci. 2020 Jul 16;1:81-91. doi: 10.1016/j.jvssci.2020.06.002. eCollection 2020. JVS Vasc Sci. 2020. PMID: 34617040 Free PMC article.
-
Membrane structures and functional correlates in the bi-segmented eye lens of the cephalopod.Biol Open. 2024 Sep 15;13(9):bio060445. doi: 10.1242/bio.060445. Epub 2024 Aug 29. Biol Open. 2024. PMID: 39133170 Free PMC article.
-
Zebrafish: An In Vivo Screening Model to Study Ocular Phenotypes.Transl Vis Sci Technol. 2022 Mar 2;11(3):17. doi: 10.1167/tvst.11.3.17. Transl Vis Sci Technol. 2022. PMID: 35285860 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Morner CT. Untersuchungen der Proteinsubstanzen in den lichtbrechenden Medien des Auges. Z Physiol Chem. 1893;18:61–106.
-
- Graw J. Genetics of crystallins: Cataract and beyond. Exp Eye Research. 2009;88:173–189. - PubMed
-
- Pierscionek BK. Bass M, Enoch J, Mahajan VN, DeCustatis C, Lakshminarayanan V, editors. Gradient index of refraction (GRIN) profiling of the eye lens. Handbook of Optics vol III Vision and Visual Optics. 2009. pp. 19.1–19.18. McGraw-Hill, New York.
-
- Pierscionek BK, Smith G, Augusteyn RC. The refractive increments of bovine α-, β- and γ-crystallins. Vision Research. 1987;27:1539–1541. - PubMed
-
- Nakao S, Fujimoto S, Nagata R, Iwata K. Model of refractive-index distribution in the rabbit crystalline lens. Opt Soc Am. 1968;58:1125–1130. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

