Common-path low-coherence interferometry fiber-optic sensor guided microincision
- PMID: 21950912
- PMCID: PMC3188640
- DOI: 10.1117/1.3622492
Common-path low-coherence interferometry fiber-optic sensor guided microincision
Abstract
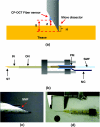
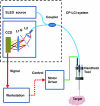
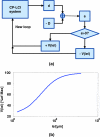
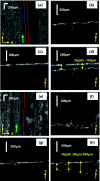
We propose and demonstrate a common-path low-coherence interferometry (CP-LCI) fiber-optic sensor guided precise microincision. The method tracks the target surface and compensates the tool-to-surface relative motion with better than ± 5 μm resolution using a precision micromotor connected to the tool tip. A single-fiber distance probe integrated microdissector was used to perform an accurate 100 μm incision into the surface of an Intralipid phantom. The CP-LCI guided incision quality in terms of depth was evaluated afterwards using three-dimensional Fourier-domain optical coherence tomography imaging, which showed significant improvement of incision accuracy compared to free-hand-only operations.
Figures

References
-
- Riviere C. N., Ang W. T., and Khosla P. K., “Toward active tremor canceling in handheld microsurgical instruments,” IEEE Trans. Rob. Autom. 19, 793–800 (2003).10.1109/TRA.2003.817506 - DOI
-
- Rizzo S., Patelli F., and Chow D. R., Vitreo-retinal Surgery, Springer-Verlag, Berlin Heidelberg: (2009).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

