The collagen-binding protein of Streptococcus mutans is involved in haemorrhagic stroke
- PMID: 21952219
- PMCID: PMC3220351
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms1491
The collagen-binding protein of Streptococcus mutans is involved in haemorrhagic stroke
Abstract
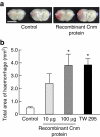
Although several risk factors for stroke have been identified, one-third remain unexplained. Here we show that infection with Streptococcus mutans expressing collagen-binding protein (CBP) is a potential risk factor for haemorrhagic stroke. Infection with serotype k S. mutans, but not a standard strain, aggravates cerebral haemorrhage in mice. Serotype k S. mutans accumulates in the damaged, but not the contralateral hemisphere, indicating an interaction of bacteria with injured blood vessels. The most important factor for high-virulence is expression of CBP, which is a common property of most serotype k strains. The detection frequency of CBP-expressing S. mutans in haemorrhagic stroke patients is significantly higher than in control subjects. Strains isolated from haemorrhagic stroke patients aggravate haemorrhage in a mouse model, indicating that they are haemorrhagic stroke-associated. Administration of recombinant CBP causes aggravation of haemorrhage. Our data suggest that CBP of S. mutans is directly involved in haemorrhagic stroke.
Figures


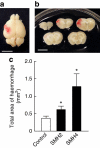
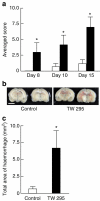
References
-
- Murray C. J. & Lopez A. D. Mortality by cause for eight regions of the world: global burden of disease study. Lancet 349, 1269–1276 (1997). - PubMed
-
- Donnan G. A., Fisher M., Macleod M. & Davis S. M. Stroke. Lancet 371, 1612–1623 (2008). - PubMed
-
- Broderick J. et al.. Guidelines for the management of spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage in adults: 2007 update: A guideline from the American Heart Association, American Stroke Association Stroke Council, High Blood Pressure Research Council, and the Quality of Care and Outcomes in Research Interdisciplinary Working Group. Stroke 38, 2001–2023 (2007). - PubMed
-
- Woo D. et al.. Genetic and environmental risk factors for intracerebral hemorrhage: preliminary results of a population-based study. Stroke 33, 1190–1195 (2002). - PubMed
-
- Emsley H. C. & Tyrrell P. J. Inflammation and infection in clinical stroke. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 22, 1399–1419 (2002). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

