A phase I, open-label, randomized crossover study to assess the effect of dosing of the MEK 1/2 inhibitor Selumetinib (AZD6244; ARRY-142866) in the presence and absence of food in patients with advanced solid tumors
- PMID: 21953275
- PMCID: PMC3220813
- DOI: 10.1007/s00280-011-1732-7
A phase I, open-label, randomized crossover study to assess the effect of dosing of the MEK 1/2 inhibitor Selumetinib (AZD6244; ARRY-142866) in the presence and absence of food in patients with advanced solid tumors
Abstract
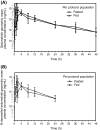
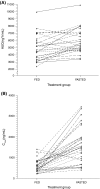
Purpose: This Phase I study assessed whether food influences the rate and extent of selumetinib absorption in patients with advanced solid malignancies and determined the safety, tolerability, and pharmacokinetic (PK) profile of selumetinib and its active metabolite N-desmethyl-selumetinib in fed and fasted states.
Methods: A single dose of 75 mg selumetinib was to be taken with food on Day 1 followed by a single dose of 75 mg after fasting for at least 10 h on Day 8, or vice versa, followed by twice daily dosing of 75 mg selumetinib from Day 10. Plasma concentrations and PK parameters were determined on Days 1 and 8. Patients could continue to receive selumetinib for as long as they benefitted from treatment.
Results: In total, 31 patients were randomized to receive selumetinib; 15 to fed/fasted sequence and 16 to fasted/fed sequence. Comprehensive PK sampling was performed on 11 and 10 patients, respectively. The geometric least-squares means of C(max) and AUC for selumetinib were reduced by 62% (ratio 0.38 90% CI 0.29, 0.50) and 19% (ratio 0.81 90% CI 0.74, 0.88), respectively, under fed compared with fasting conditions. The rate of absorption (t(max)) of selumetinib (fed) was delayed by approximately 2.5 h (median). The food effect was also observed for the active metabolite N-desmethyl-selumetinib. Selumetinib was well tolerated.
Conclusions: The presence of food decreased the extent of absorption of selumetinib. It is recommended that for further clinical studies, selumetinib be taken on an empty stomach. Selumetinib demonstrated an acceptable safety profile in the advanced cancer population.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A phase I dose-escalation study of selumetinib in combination with docetaxel or dacarbazine in patients with advanced solid tumors.BMC Cancer. 2017 Mar 6;17(1):173. doi: 10.1186/s12885-017-3143-6. BMC Cancer. 2017. PMID: 28264648 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Comparison of the Pharmacokinetics of the Phase II and Phase III Capsule Formulations of Selumetinib and the Effects of Food on Exposure: Results From Two Randomized Crossover Trials in Healthy Male Subjects.Clin Ther. 2017 Nov;39(11):2260-2275.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2017.08.022. Epub 2017 Oct 4. Clin Ther. 2017. PMID: 28985960 Clinical Trial.
-
Phase I pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic study of the oral, small-molecule mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 1/2 inhibitor AZD6244 (ARRY-142886) in patients with advanced cancers.J Clin Oncol. 2008 May 1;26(13):2139-46. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2007.14.4956. Epub 2008 Apr 7. J Clin Oncol. 2008. PMID: 18390968 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Selumetinib in the treatment of non-small-cell lung cancer.Future Oncol. 2016 Nov;12(22):2545-2560. doi: 10.2217/fon-2016-0132. Epub 2016 Jul 28. Future Oncol. 2016. PMID: 27467210 Review.
-
Selumetinib: First Approval.Drugs. 2020 Jun;80(9):931-937. doi: 10.1007/s40265-020-01331-x. Drugs. 2020. PMID: 32504375 Review.
Cited by
-
Effect of food on selumetinib pharmacokinetics and gastrointestinal tolerability in adolescents with neurofibromatosis type 1-related plexiform neurofibromas.Neurooncol Adv. 2024 Mar 16;6(1):vdae036. doi: 10.1093/noajnl/vdae036. eCollection 2024 Jan-Dec. Neurooncol Adv. 2024. PMID: 38721358 Free PMC article.
-
Phase II Study of Selumetinib in Children and Young Adults With Tumors Harboring Activating Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Pathway Genetic Alterations: Arm E of the NCI-COG Pediatric MATCH Trial.J Clin Oncol. 2022 Jul 10;40(20):2235-2245. doi: 10.1200/JCO.21.02840. Epub 2022 Apr 1. J Clin Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35363510 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
A phase I dose-escalation study of Selumetinib in combination with Erlotinib or Temsirolimus in patients with advanced solid tumors.Invest New Drugs. 2017 Oct;35(5):576-588. doi: 10.1007/s10637-017-0459-7. Epub 2017 Apr 19. Invest New Drugs. 2017. PMID: 28424891 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
A phase I dose-escalation study of selumetinib in combination with docetaxel or dacarbazine in patients with advanced solid tumors.BMC Cancer. 2017 Mar 6;17(1):173. doi: 10.1186/s12885-017-3143-6. BMC Cancer. 2017. PMID: 28264648 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
A Combined Antitumor Strategy Mediated by a New Targeted Nanosystem to Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Int J Nanomedicine. 2021 May 18;16:3385-3405. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S302288. eCollection 2021. Int J Nanomedicine. 2021. PMID: 34040370 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ramnath N, Adjei A. Inhibitors of Raf kinase and MEK signaling. Update Cancer Ther. 2007;2:111–118. doi: 10.1016/j.uct.2007.10.001. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources