Characterization of the nature of granulocytic myeloid-derived suppressor cells in tumor-bearing mice
- PMID: 21954284
- PMCID: PMC3250305
- DOI: 10.1189/jlb.0311177
Characterization of the nature of granulocytic myeloid-derived suppressor cells in tumor-bearing mice
Abstract
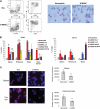
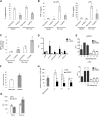
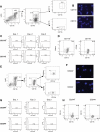
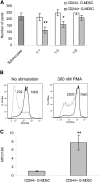
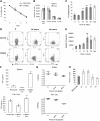
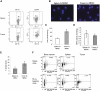
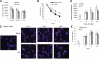
MDSCs are a group of cells with potent immune-suppressive activity. These cells accumulate in many pathologic conditions and play a major role in the regulation of immune responses. The nature of MDSC remains highly debatable. In cancer, most MDSCs are represented by cells with granulocytic phenotype and morphology, G-MDSC. The relationship between G-MDSCs and Neu remains unclear. In this study, we have found that G-MDSCs, from tumor-bearing, and Neu, from tumor-free, mice share a common morphology and phenotype. However, in contrast to Neu, a substantial proportion of G-MDSCs expressed M-CSFR and a CD244 molecule. Neu had significantly higher phagocytic activity, expression of lysosomal proteins, and TNF-α than corresponding G-MDSCs, which had significantly higher activity of arginase, MPO, and ROS. In contrast to G-MDSC, neither rested nor mobilized Neu suppressed T cells. G-MDSC survived 2 days in culture in the presence of GM-CSF and within 24 h, became phenotypic and functionally similar to Neu. Tumor-associated G-MDSC shared most characteristics of splenic G-MDSC, rather then Neu. These data suggest that in cancer, despite morphological and phenotypic similarities, G-MDSCs are functionally distinct from Neu and are comprised of pathologically activated precursors of Neu.
Figures
References
-
- Peranzoni E., Zilio S., Marigo I., Dolcetti L., Zanovello P., Mandruzzato S., Bronte V. (2010) Myeloid-derived suppressor cell heterogeneity and subset definition. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 22, 238–244 - PubMed
-
- Shojaei F., Wu X., Malik A. K., Zhong C., Baldwin M. E., Schanz S., Fuh G., Gerber H. P., Ferrara N. (2007) Tumor refractoriness to anti-VEGF treatment is mediated by CD11b(+)Gr1(+) myeloid cells. Nat. Biotechnol. 25, 911–920 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

