Workflow and metrics for image quality control in large-scale high-content screens
- PMID: 21956170
- PMCID: PMC3593271
- DOI: 10.1177/1087057111420292
Workflow and metrics for image quality control in large-scale high-content screens
Abstract
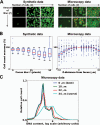
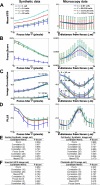
Automated microscopes have enabled the unprecedented collection of images at a rate that precludes visual inspection. Automated image analysis is required to identify interesting samples and extract quantitative information for high-content screening (HCS). However, researchers are impeded by the lack of metrics and software tools to identify image-based aberrations that pollute data, limiting experiment quality. The authors have developed and validated approaches to identify those image acquisition artifacts that prevent optimal extraction of knowledge from high-content microscopy experiments. They have implemented these as a versatile, open-source toolbox of algorithms and metrics readily usable by biologists to improve data quality in a wide variety of biological experiments.
Figures


References
-
- Vaisberg EA, Lenzi D, Hansen RL, Keon BH, Finer JT. An infrastructure for high-throughput microscopy: instrumentation, informatics, and integration. Methods Enzymol. 2006;414:484–512. - PubMed
-
- Lehmussola A, Selinummi J, Ruusuvuori P, Niemisto A, Yli-Harja O. Simulating fluorescent microscope images of cell populations. Conf Proc IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2005;3:3153–3156. - PubMed
-
- Sun Y, Duthaler S, Nelson BJ. Autofocusing in computer microscopy: selecting the optimal focus algorithm. Microsc Res Tech. 2004;65:139–149. - PubMed
-
- Fuller CJ, Straight AF. Image analysis benchmarking methods for high-content screen design. J Microsc. 2010;238:145–161. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

