Functions and mechanisms of spliceosomal small nuclear RNA pseudouridylation
- PMID: 21957045
- PMCID: PMC4161978
- DOI: 10.1002/wrna.77
Functions and mechanisms of spliceosomal small nuclear RNA pseudouridylation
Abstract
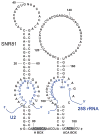
Pseudouridines are the most abundant and highly conserved modified nucleotides identified in spliceosomal small nuclear RNAs (snRNAs). Most pseudouridines are also clustered in functionally important regions of spliceosomal snRNAs. Experiments carried out in several independent experimental systems show that the pseudouridines in spliceosomal snRNAs are functionally important for pre-messenger RNA (mRNA) splicing. Experimental data also indicate that spliceosomal snRNA pseudouridylation can be catalyzed by both RNA-dependent (box H/ACA Ribonucleoproteins) and RNA-independent (protein-only enzymes) mechanisms.
Copyright © 2011 John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
Figures
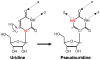

References
-
- Cohn WE, Volkin W. Nucleoside-5′-phosphates from ribonucleic acid. Nature (London) 1951;167:483–484.
-
- Davis FF, Allen FW. Ribonucleic acids from yeast which contain a fifth nucleotide. J Biol Chem. 1957;227:907–915. - PubMed
-
- Lane BG. Historical perspectives on RNA nucleoside modifications. In: Grosjean H, Benne R, editors. Modification and Editing of RNA. Washington, DC: ASM Press; 1998. pp. 1–20.
-
- Arnez JG, Steitz TA. Crystal structure of unmodified tRNA(Gln) complexed with glutaminyl-tRNA synthetase and ATP suggests a possible role for pseudouridines in stabilization of RNA structure. Biochemistry. 1994;33:7560–7567. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

