Scale-free properties of the functional magnetic resonance imaging signal during rest and task
- PMID: 21957241
- PMCID: PMC3197021
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2111-11.2011
Scale-free properties of the functional magnetic resonance imaging signal during rest and task
Abstract
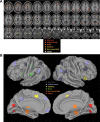
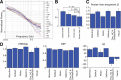
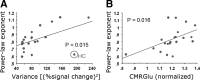
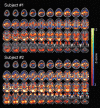
It has been shown recently that a significant portion of brain electrical field potentials consists of scale-free dynamics. These scale-free brain dynamics contain complex spatiotemporal structures and are modulated by task performance. Here we show that the fMRI signal recorded from the human brain is also scale free; its power-law exponent differentiates between brain networks and correlates with fMRI signal variance and brain glucose metabolism. Importantly, in parallel to brain electrical field potentials, the variance and power-law exponent of the fMRI signal decrease during task activation, suggesting that the signal contains more long-range memory during rest and conversely is more efficient at online information processing during task. Remarkably, similar changes also occurred in task-deactivated brain regions, revealing the presence of an optimal dynamic range in the fMRI signal. The scale-free properties of the fMRI signal and brain electrical field potentials bespeak their respective stationarity and nonstationarity. This suggests that neurovascular coupling mechanism is likely to contain a transformation from nonstationarity to stationarity. In summary, our results demonstrate the functional relevance of scale-free properties of the fMRI signal and impose constraints on future models of neurovascular coupling.
Figures


References
-
- Bak P. How nature works. New York: Springer; 1996.
-
- Beran J. Statistics for long-memory processes. Boca Raton, FL: Chapman and Hall/CRC; 1994.
-
- Biswal B, Yetkin FZ, Haughton VM, Hyde JS. Functional connectivity in the motor cortex of resting human brain using echo-planar MRI. Magn Reson Med. 1995;34:537–541. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
