Inhibitory effects of bile acids and synthetic farnesoid X receptor agonists on rotavirus replication
- PMID: 21957312
- PMCID: PMC3209393
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.05839-11
Inhibitory effects of bile acids and synthetic farnesoid X receptor agonists on rotavirus replication
Abstract
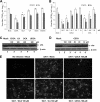
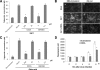
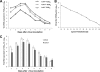
Rotaviruses (group A rotaviruses) are the most important cause of severe gastroenteritis in infants and children worldwide. Currently, an antiviral drug is not available and information on therapeutic targets for antiviral development is limited for rotavirus infection. Previously, it was shown that lipid homeostasis is important in rotavirus replication. Since farnesoid X receptor (FXR) and its natural ligands bile acids (such as chenodeoxycholic acid [CDCA]) play major roles in cholesterol and lipid homeostasis, we examined the effects of bile acids and synthetic FXR agonists on rotavirus replication in association with cellular lipid levels. In a mouse model of rotavirus infection, effects of oral administration of CDCA on fecal rotavirus shedding were investigated. The results demonstrate the following. First, the intracellular contents of triglycerides were significantly increased by rotavirus infection. Second, CDCA, deoxycholic acid (DCA), and other synthetic FXR agonists, such as GW4064, significantly reduced rotavirus replication in cell culture in a dose-dependent manner. The reduction of virus replication correlated positively with activation of the FXR pathway and reduction of cellular triglyceride contents (r(2) = 0.95). Third, oral administration of CDCA significantly reduced fecal virus shedding in mice (P < 0.05). We conclude that bile acids and FXR agonists play important roles in the suppression of rotavirus replication. The inhibition mechanism is proposed to be the downregulation of lipid synthesis induced by rotavirus infection.
Figures

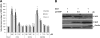
Similar articles
-
Bile acids induce the expression of the human peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha gene via activation of the farnesoid X receptor.Mol Endocrinol. 2003 Feb;17(2):259-72. doi: 10.1210/me.2002-0120. Mol Endocrinol. 2003. PMID: 12554753
-
Farnesoid X receptor activation by chenodeoxycholic acid induces detoxifying enzymes through AMP-activated protein kinase and extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2-mediated phosphorylation of CCAAT/enhancer binding protein β.Drug Metab Dispos. 2011 Aug;39(8):1451-9. doi: 10.1124/dmd.111.038414. Epub 2011 May 19. Drug Metab Dispos. 2011. PMID: 21596890
-
Human kininogen gene is transactivated by the farnesoid X receptor.J Biol Chem. 2003 Aug 1;278(31):28765-70. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M304568200. Epub 2003 May 21. J Biol Chem. 2003. PMID: 12761213
-
Rotavirus replication and the role of cellular lipid droplets: New therapeutic targets?J Formos Med Assoc. 2016 Jun;115(6):389-94. doi: 10.1016/j.jfma.2016.02.004. Epub 2016 Mar 24. J Formos Med Assoc. 2016. PMID: 27017233 Review.
-
Bile acid nuclear receptor FXR and digestive system diseases.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2015 Mar;5(2):135-44. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2015.01.004. Epub 2015 Feb 25. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2015. PMID: 26579439 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The intestinal regionalization of acute norovirus infection is regulated by the microbiota via bile acid-mediated priming of type III interferon.Nat Microbiol. 2020 Jan;5(1):84-92. doi: 10.1038/s41564-019-0602-7. Epub 2019 Nov 25. Nat Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 31768030 Free PMC article.
-
Upregulation of bile acid receptor TGR5 and nNOS in gastric myenteric plexus is responsible for delayed gastric emptying after chronic high-fat feeding in rats.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2015 May 15;308(10):G863-73. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00380.2014. Epub 2014 Dec 24. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2015. PMID: 25540233 Free PMC article.
-
The crucial role of bile acids in the entry of porcine enteric calicivirus.Virology. 2014 May;456-457:268-78. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2014.04.002. Epub 2014 Apr 19. Virology. 2014. PMID: 24889246 Free PMC article.
-
Epidemiology, pathogenesis, immune evasion mechanism and vaccine development of porcine Deltacoronavirus.Funct Integr Genomics. 2024 Apr 24;24(3):79. doi: 10.1007/s10142-024-01346-7. Funct Integr Genomics. 2024. PMID: 38653845 Review.
-
Taurolithocholic acid protects against viral haemorrhagic fever via inhibition of ferroptosis.Nat Microbiol. 2024 Oct;9(10):2583-2599. doi: 10.1038/s41564-024-01801-y. Epub 2024 Sep 18. Nat Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39294459
References
-
- Akashi Y., Miyazaki H., Nakayama F. 1983. Correlation of bile acid composition between liver tissue and bile. Clin. Chim. Acta 133:125–132 - PubMed
-
- Anisfeld A. M., et al. 2003. Syndecan-1 expression is regulated in an isoform-specific manner by the farnesoid-X receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 278:20420–20428 - PubMed
-
- Bligh E. G., Dyer W. J. 1959. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can. J. Biochem. Physiol. 37:911–917 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

