Biogenesis and assembly of eukaryotic cytochrome c oxidase catalytic core
- PMID: 21958598
- PMCID: PMC3262112
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbabio.2011.09.005
Biogenesis and assembly of eukaryotic cytochrome c oxidase catalytic core
Abstract
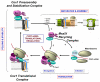
Eukaryotic cytochrome c oxidase (COX) is the terminal enzyme of the mitochondrial respiratory chain. COX is a multimeric enzyme formed by subunits of dual genetic origin which assembly is intricate and highly regulated. The COX catalytic core is formed by three mitochondrial DNA encoded subunits, Cox1, Cox2 and Cox3, conserved in the bacterial enzyme. Their biogenesis requires the action of messenger-specific and subunit-specific factors which facilitate the synthesis, membrane insertion, maturation or assembly of the core subunits. The study of yeast strains and human cell lines from patients carrying mutations in structural subunits and COX assembly factors has been invaluable to identify these ancillary factors. Here we review the current state of knowledge of the biogenesis and assembly of the eukaryotic COX catalytic core and discuss the degree of conservation of the players and mechanisms operating from yeast to human. This article is part of a Special Issue entitled: Biogenesis/Assembly of Respiratory Enzyme Complexes.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures

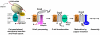
References
-
- Hill BC. Modeling the sequence of electron transfer reactions in the single turnover of reduced, mammalian cytochrome c oxidase with oxygen. J. Biol. Chem. 1994;269:2419–2425. - PubMed
-
- Brunori M, Giuffre A, Malatesta F, Sarti P. Investigating the mechanism of electron transfer to the binuclear center in Cu-heme oxidases. J. Bioenerg. Biomembr. 1998;30:41–45. - PubMed
-
- Brunori M, Giuffre A, Sarti P. Cytochrome c oxidase, ligands and electrons. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2005;99:324–336. - PubMed
-
- Belevich I, Verkhovsky MI, Wikstrom M. Proton-coupled electron transfer drives the proton pump of cytochrome c oxidase. Nature. 2006;440:829–832. - PubMed
-
- Yoshikawa S, Muramoto K, Shinzawa-Itoh K, Aoyama H, Tsukihara T, Shimokata K, Katayama Y, Shimada H. Proton pumping mechanism of bovine heart cytochrome c oxidase. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2006;1757:1110–1116. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

