A role for aberrantly expressed nuclear localized decorin in migration and invasion of dysplastic and malignant oral epithelial cells
- PMID: 21958730
- PMCID: PMC3198745
- DOI: 10.1186/1758-3284-3-44
A role for aberrantly expressed nuclear localized decorin in migration and invasion of dysplastic and malignant oral epithelial cells
Abstract
Background: Oral cancer is the sixth most common malignancy worldwide with a mortality rate that is higher than many other cancers. Death usually occurs as a result of local invasion and regional lymph node metastases. Decorin is a multifunctional proteoglycan of the extracellular matrix that affects the biology of various types of cancer. Previously; we have shown that decorin is aberrantly expressed in the nucleus in human dysplastic oral keratinocytes (DOK) and malignant squamous cells carcinoma (SCC-25) and human biopsy tissues. In this study, we examined the role of nuclear decorin in oral cancer progression.
Materials and methods: We have used a post-transcriptional gene silencing (RNA interference) approach to stably knockdown nuclear decorin gene expression in DOK and SCC-25 cells using a specific shRNA plasmid and a combination of immunological and molecular techniques to study nuclear decorin function in these oral epithelial cell lines.
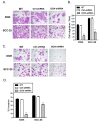
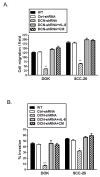
Results: More than 80% decorin silencing/knockdown was achieved as confirmed by real time PCR and western blot analysis in both DOK and SCC-25 cells. This RNA interference-mediated knockdown of nuclear decorin expression resulted in significantly reduced invasion and migration in these cell lines as measured by Matrigel™ coated and uncoated Trans well chamber assays respectively. Decorin silencing also resulted in reduced IL-8 mRNA and proteins levels in these cell lines. Culturing decorin silenced DOK and SCC-25 cells, with recombinant human IL-8 or IL-8 containing conditioned medium from respective un-transfected cells for 24 h prior to migration and invasion experiments, resulted in the salvation of reduced migration and invasion phenotype. Furthermore, we found that nuclear localized decorin interacts with EGFR in the nuclear fractions of both DOK and SCC-25 cells. Interestingly, EGFR (trans) activation has previously been shown to be involved in IL-8 production in various epithelia.
Conclusions: Taken together, our results indicate that nuclear localized decorin plays an important role in migration and invasion of oral cancer cells and thus may present as a novel potential target for the treatment of oral cancer.
Figures


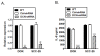

Similar articles
-
Knockdown of aberrantly expressed nuclear localized decorin attenuates tumour angiogenesis related mediators in oral cancer progression model in vitro.Head Neck Oncol. 2012 Jun 8;4:11. doi: 10.1186/1758-3284-4-11. Head Neck Oncol. 2012. PMID: 22507529 Free PMC article.
-
Aberrant expression and localization of decorin in human oral dysplasia and squamous cell carcinoma.Cancer Res. 2003 Nov 15;63(22):7769-76. Cancer Res. 2003. PMID: 14633702
-
EMMPRIN/CD147 up-regulates urokinase-type plasminogen activator: implications in oral tumor progression.BMC Cancer. 2012 Mar 23;12:115. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-12-115. BMC Cancer. 2012. PMID: 22443116 Free PMC article.
-
MIEN1 promotes oral cancer progression and implicates poor overall survival.Cancer Biol Ther. 2015;16(6):876-85. doi: 10.1080/15384047.2015.1040962. Cancer Biol Ther. 2015. PMID: 25996585 Free PMC article.
-
Decorin: matrix-based pan-cancer tumor suppressor.Mol Cell Biochem. 2025 Jun;480(6):3569-3591. doi: 10.1007/s11010-025-05224-z. Epub 2025 Feb 15. Mol Cell Biochem. 2025. PMID: 39954173 Review.
Cited by
-
An essential role for decorin in bladder cancer invasiveness.EMBO Mol Med. 2013 Dec;5(12):1835-51. doi: 10.1002/emmm.201302655. Epub 2013 Oct 20. EMBO Mol Med. 2013. PMID: 24142880 Free PMC article.
-
Decorin is responsible for progression of non-small-cell lung cancer by promoting cell proliferation and metastasis.Tumour Biol. 2015 May;36(5):3345-54. doi: 10.1007/s13277-014-2968-8. Epub 2014 Dec 20. Tumour Biol. 2015. PMID: 25524578
-
Deregulation of decorin and FHL1 are associated with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma progression and poor prognosis.Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015 Nov 15;8(11):20965-70. eCollection 2015. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015. PMID: 26885026 Free PMC article.
-
Opticin, a small leucine-rich proteoglycan, is uniquely expressed and translocated to the nucleus of chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells.Exp Hematol Oncol. 2013 Aug 28;2(1):23. doi: 10.1186/2162-3619-2-23. Exp Hematol Oncol. 2013. PMID: 24499526 Free PMC article.
-
Research progress on the role of decorin in the development of oral mucosal carcinogenesis.Oncol Res. 2025 Feb 28;33(3):577-590. doi: 10.32604/or.2024.053119. eCollection 2025. Oncol Res. 2025. PMID: 40109852 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Cooper JS, Pajak TF, Forastiere AA, Jacobs J, Campbell BH, Saxman SB, Kish JA, Kim HE, Cmelak AJ, Rotman M. et al.Postoperative concurrent radiotherapy and chemotherapy for high-risk squamous-cell carcinoma of the head and neck. N Engl J Med. 2004;350:1937–1944. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa032646. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

