Curcumin nanoformulations: a future nanomedicine for cancer
- PMID: 21959306
- PMCID: PMC3259195
- DOI: 10.1016/j.drudis.2011.09.009
Curcumin nanoformulations: a future nanomedicine for cancer
Abstract
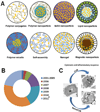
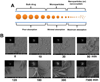
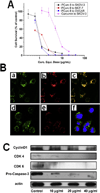
Curcumin, a natural diphenolic compound derived from turmeric Curcuma longa, has proven to be a modulator of intracellular signaling pathways that control cancer cell growth, inflammation, invasion and apoptosis, revealing its anticancer potential. In this review, we focus on the design and development of nanoparticles, self-assemblies, nanogels, liposomes and complex fabrication for sustained and efficient curcumin delivery. We also discuss the anticancer applications and clinical benefits of nanocurcumin formulations. Only a few novel multifunctional and composite nanosystem strategies offer simultaneous therapy as well as imaging characteristics. We also summarize the challenges to developing curcumin delivery platforms and up-to-date solutions for improving curcumin bioavailability and anticancer potential for therapy.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Maheshwari RK, et al. Multiple biological activities of curcumin: a short review. Life Sci. 2006;78:2081–2087. - PubMed
-
- Goel A, et al. Curcumin as ‘curecumin’: from kitchen to clinic. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2008;75:787–809. - PubMed
-
- Kunnumakkara AB, et al. Curcumin inhibits proliferation, invasion, angiogenesis and metastasis of different cancers through interaction with multiple cell signaling proteins. Cancer Lett. 2008;269:199–225. - PubMed
-
- Landis-Piwowar KR, et al. The proteasome as a potential target for novel anticancer drugs and chemosensitizers. Drug Resist. Update. 2006;9:263–273. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

