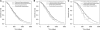Cost-effectiveness analysis of trastuzumab to treat HER2-positive advanced gastric cancer based on the randomised ToGA trial
- PMID: 21959871
- PMCID: PMC3241558
- DOI: 10.1038/bjc.2011.390
Cost-effectiveness analysis of trastuzumab to treat HER2-positive advanced gastric cancer based on the randomised ToGA trial
Abstract
Background: We performed a cost-effectiveness analysis of trastuzumab plus chemotherapy for human epidermal growth factor type-2 (HER2)-positive advanced gastric cancer (GC) based on data obtained from the Trastuzumab for Gastric Cancer (ToGA) trial from a Japanese perspective.
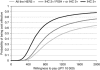
Methods: The following Japanese and Korean populations of the ToGA trial were analysed to obtain mean overall and progression-free survival times: (1) all HER2-positive populations, (2) immunohistochemical (IHC) 2+/fluorescence in situ hybridisation (FISH)+ or IHC 3+ populations, and (3) IHC 3+ only population. The effect of trastuzumab treatment on mean survival time was estimated by fitting a Weibull parametric function. Costs were calculated from the perspective of health-care payer. Neither costs nor outcomes were discounted because of short life expectancy.
Results: In the base-case analysis, the incremental cost-effectiveness ratio was (1) JPY 12 million (€110,000) per quality-adjusted life year (QALY) gained and JPY 8.9 million (€81,000) per life-year gained (LYG) for all HER2-positive populations, (2) JPY 9.1 million (€83,000) per QALY gained and JPY 6.6 million (€60,000) per LYG for the IHC 2+/FISH+ or IHC 3+ population, and (3) JPY 6.1 million (€55,000) per QALY gained and JPY 4.3 million (€39,000) per LYG for the IHC 3+ population.
Conclusion: Trastuzumab treatment for IHC 3+ populations is cost effective. Our analysis can find a cost-effective subgroup when advanced GC is treated by trastuzumab.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Bang YJ, Van Cutsem E, Feyereislova A, Chung HC, Shen L, Sawaki A, Lordick F, Ohtsu A, Omuro Y, Satoh T, Aprile G, Kulikov E, Hill J, Lehle M, Ruschoff J, Kang YK (2010) Trastuzumab in combination with chemotherapy versus chemotherapy alone for treatment of HER2-positive advanced gastric or gastro-oesophageal junction cancer (ToGA): a phase 3, open-label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet 376(9742): 687–697 - PubMed
-
- Cunningham D, Starling N, Rao S, Iveson T, Nicolson M, Coxon F, Middleton G, Daniel F, Oates J, Norman AR (2008) Capecitabine and oxaliplatin for advanced esophagogastric cancer. N Engl J Med 358(1): 36–46 - PubMed
-
- Department of Health (2010) A New Value-Based Approach to the Pricing of Branded Medicines. Department of Health: London
-
- Efron B, Tibshirani RJ (1994) An Introduction to the Bootstrap. Chapman and Hall/CRC: London
-
- Ferlay J, Shin HR, Bray F, Forman D, Mathers C, Parkin DM (2010) Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in 2008: GLOBOCAN 2008. Int J Cancer 127(12): 2893–2917 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous