A multicenter retrospective experience of infliximab in Crohn's disease patients: infusion reaction rates and treatment persistency
- PMID: 21960854
- PMCID: PMC3099319
A multicenter retrospective experience of infliximab in Crohn's disease patients: infusion reaction rates and treatment persistency
Abstract
Background: Infusion reactions have been associated with infliximab therapy, but no study has assessed how physicians treat and manage this common adverse event.
Goals: To determine how gastroenterologists manage infusion reactions, identify prophylactic pretreatment protocols, and determine infliximab treatment persistence in the presence of infusion reactions.
Method: This retrospective multicenter chart review analyzed data from adults younger than 90 years at the time of their first infliximab infusion from 9 academic or community-based gastroenterology practices. Infusion reaction rates were compared using a Chi-square test with Yates' correction. Kaplan-Meier methods assessed infliximab treatment persistency.
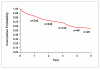
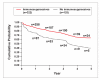
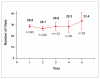
Results: Among 6,468 infusions with known infusion reaction status administered to 447 patients, 3.5% (226/6,468) of infusions resulted in an infusion reaction, and less than 0.1% (2/6,468) were associated with a serious infusion reaction. Among all patients, 19.7% (88/447) experienced at least 1 infusion reaction, whereas 0.4% (2/447) experienced a serious infusion reaction. Patients receiving concomitant immunosuppressives had fewer infusion reactions compared to patients not receiving them (57/322 patients, 17.7% vs 31/125 patients, 24.8%; P=.118). The cumulative proportion of patients continuing infliximab therapy at 2, 4, and 5 years was 73%, 58%, and 54%, respectively.
Conclusions: The incidence of serious infusion reactions was low. In the overall experience observed in this clinical practice retrospective cohort, no conclusions can be drawn regarding the effectiveness of specific infusion reaction prophylactic measures. In spite of infusion reactions, the long-term infliximab treatment persistence rate was high.
Keywords: Infliximab; infusion reaction; prophylaxis; treatment persistency.
Figures
References
-
- Sewitch JM, Abrahamowicz A, Barkun A, et al. Patient nonadherence to medication in inflammatory bowel disease. Am J Gastroenterol. 2003;98:1535–1544. - PubMed
-
- Hanauer S, Feagan B, Lichtenstein G, et al. Maintenance infliximab for Crohn's disease: the ACCENT I randomised trial. Lancet. 2002;359:1541–1549. - PubMed
-
- Rutgeerts P, Feagan BG, Lichtenstein GR, et al. Comparison of scheduled and episodic treatment strategies of infliximab in Crohn's disease. Gastroenterology. 2004;126:402–413. - PubMed
-
- Sands BE, Anderson FH, Bernstein CN, et al. Infliximab maintenance therapy for fistulizing Crohn's disease. N Engl J Med. 2004;350:876–885. - PubMed
-
- Colombel JF, Loftus EV, Jr, Termaine WJ, et al. The safety profile of infliximab in patients with Crohn's disease: the Mayo Clinic experience in 500 patients. Gastroenterology. 2004;126:19–31. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
