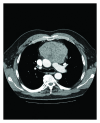
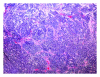
An incidentaloma: primitive neuroectodermal tumor of the thymus
- PMID: 21961013
- PMCID: PMC3180864
- DOI: 10.1155/2011/407523
An incidentaloma: primitive neuroectodermal tumor of the thymus
Abstract
After presenting for a routine screening exam, and 57-year-old man was diagnosed with an incidentaloma-a primitive neuroectodermal tumor (PNET) of the thymus. A member of the Ewing sarcoma family of tumors, a PNET is typically regarded as a malignancy of childhood and adolescence, usually occurring in the central nervous system. In the case at hand, our patient had an extremely unusual presentation, given his age and tumor location. Initial presentation is the only predictor for long-term survival. Current treatment recommendations advocate complete surgical resection whenever possible, radiation therapy, and adjuvant versus neoadjuvant chemotherapy.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Adult soft tissue Ewing sarcoma or primitive neuroectodermal tumors: predictors of survival?Arch Surg. 2003 Mar;138(3):281-5. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.138.3.281. Arch Surg. 2003. PMID: 12611575
-
Ewing sarcoma/primitive neuroectodermal tumor of the kidney treated with chemotherapy including ifosfamide.Pediatr Int. 2016 Aug;58(8):766-9. doi: 10.1111/ped.12963. Epub 2016 Jun 21. Pediatr Int. 2016. PMID: 27324740
-
Ewing sarcoma/primitive neuroectodermal tumor of the chest wall: impact of initial versus delayed resection on tumor margins, survival, and use of radiation therapy.Ann Surg. 2003 Oct;238(4):563-7; discussion 567-8. doi: 10.1097/01.sla.0000089857.45191.52. Ann Surg. 2003. PMID: 14530727 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Primary intracranial dural-based Ewing sarcoma/peripheral primitive neuroectodermal tumor mimicking a meningioma: A rare tumor with review of literature.Asian J Neurosurg. 2017 Jul-Sep;12(3):351-357. doi: 10.4103/1793-5482.185060. Asian J Neurosurg. 2017. PMID: 28761507 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multiple Ewing Sarcoma/Primitive Neuroectodermal Tumors in the Mediastinum: A Case Report and Literature Review.Medicine (Baltimore). 2016 Feb;95(7):e2725. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000002725. Medicine (Baltimore). 2016. PMID: 26886614 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Schweigert M, Meyer C, Wolff F, Stein HJ. Peripheral primitive neuroectodermal tumor of the thymus. Interactive CardioVascular and Thoracic Surgery. 2010;12(2):303–305. - PubMed
-
- Scurr M, Judson I. How to treat the Ewing’s family of sarcomas in adult patients. Oncologist. 2006;11(1):65–72. - PubMed
-
- Luo W, Xiao EH. CT, MRI and pathologic features of peripheral primitive neuroectodermal tumors: a report of eight cases with literature review. Ai Zheng. 2008;27(6):627–632. - PubMed
-
- Winer-Muram HT, Kauffman WM, Gronemeyer SA, Jennings SG. Primitive neuroectodermal tumors of the chest wall (Askin tumors): CT and MR findings. American Journal of Roentgenology. 1993;161(2):265–268. - PubMed
-
- Martin RC, Brennan MF. Adult soft tissue ewing sarcoma or primitive neuroectodermal tumors: predictors of survival? Archives of Surgery. 2003;138(3):281–285. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources