Does self-regulation and autonomic regulation have an influence on survival in breast and colon carcinoma patients? results of a prospective outcome study
- PMID: 21961625
- PMCID: PMC3192663
- DOI: 10.1186/1477-7525-9-85
Does self-regulation and autonomic regulation have an influence on survival in breast and colon carcinoma patients? results of a prospective outcome study
Abstract
Background: Cancer Related Fatigue (CRF) and circadian rhythm have a great impact on the quality of life (HRQL) of patients with breast (BC) and colon cancer (CRC). Other patient related outcomes in oncology are measured by new instruments focusing on adaptive characteristics such as sense of coherence or self-regulation, which could be more appropriate as a prognostic tool than classical HRQL. The aim of this study was to assess the association of autonomic regulation (aR) and self-regulation (SR) with survival.
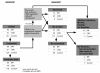
Methods: 146 cancer patients and 120 healthy controls took part in an initial evaluation in 2000/2001. At a median follow up of 5.9 years later, 62 of 95 BC, 17 of 51 CRC patients, and 85 of 117 healthy controls took part in the follow-up study. 41 participants had died. For the follow-up evaluation, participants were requested to complete the standardized aR and SR questionnaires.
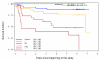
Results: On average, cancer patients had survived for 10.1 years with the disease. Using a Cox proportional hazard regression with stepwise variables such as age, diagnosis group, Charlson co-morbidity index, body mass index (BMI)) aR and SR. SR were identified as independent parameters with potential prognostic relevance on survival While aR did not significantly influence survival, SR showed a positive and independent impact on survival (OR = 0.589; 95%-CI: 0.354 - 0.979). This positive effect persisted significantly in the sensitivity analysis of the subgroup of tumour patients and in the subscale 'Achieve satisfaction and well-being' and by tendency in the UICC stages nested for the different diagnoses groups.
Conclusions: Self-regulation might be an independent prognostic factor for the survival of breast and colon carcinoma patients and merits further prospective studies.
Figures
References
-
- Astradsson E, Granath L, Heedman PA, Starkhammar H. Cancer patients hospitalised for palliative reasons. Symptoms and needs presented at a university hospital. Support Care Cancer. 2001;9(2):97–102. - PubMed
-
- Stone P, Richardson A, Ream E, Smith AG, Kerr DJ, Kearney N. Cancer-related fatigue: inevitable, unimportant and untreatable? Results of a multi-centre patient survey. Cancer Fatigue Forum. Ann Oncol. 2000;11(8):971–975. - PubMed
-
- Davidson JR, MacLean AW, Brundage MD, Schulze K. Sleep disturbance in cancer patients. Soc Sci Med. 2002;54(9):1309–1321. - PubMed
-
- Roscoe JA, Morrow GR, Hickok JT, Bushunow P, Matteson S, Rakita D, Andrews PL. Temporal interrelationships among fatigue, circadian rhythm and depression in breast cancer patients undergoing chemotherapy treatment. Support Care Cancer. 2002;10(4):329–336. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials