Role of protein kinase C and epidermal growth factor receptor signalling in growth stimulation by neurotensin in colon carcinoma cells
- PMID: 21961726
- PMCID: PMC3196723
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2407-11-421
Role of protein kinase C and epidermal growth factor receptor signalling in growth stimulation by neurotensin in colon carcinoma cells
Abstract
Background: Neurotensin has been found to promote colon carcinogenesis in rats and mice, and proliferation of human colon carcinoma cell lines, but the mechanisms involved are not clear. We have examined signalling pathways activated by neurotensin in colorectal and pancreatic carcinoma cells.
Methods: Colon carcinoma cell lines HCT116 and HT29 and pancreatic adenocarcinoma cell line Panc-1 were cultured and stimulated with neurotensin or epidermal growth factor (EGF). DNA synthesis was determined by incorporation of radiolabelled thymidine into DNA. Levels and phosphorylation of proteins in signalling pathways were assessed by Western blotting.
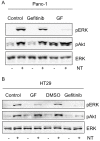
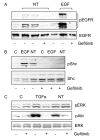
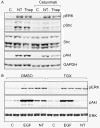
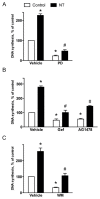
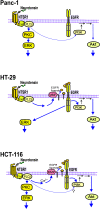
Results: Neurotensin stimulated the phosphorylation of both extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) and Akt in all three cell lines, but apparently did so through different pathways. In Panc-1 cells, neurotensin-induced phosphorylation of ERK, but not Akt, was dependent on protein kinase C (PKC), whereas an inhibitor of the β-isoform of phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K), TGX221, abolished neurotensin-induced Akt phosphorylation in these cells, and there was no evidence of EGF receptor (EGFR) transactivation. In HT29 cells, in contrast, the EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor gefitinib blocked neurotensin-stimulated phosphorylation of both ERK and Akt, indicating transactivation of EGFR, independently of PKC. In HCT116 cells, neurotensin induced both a PKC-dependent phosphorylation of ERK and a metalloproteinase-mediated transactivation of EGFR that was associated with a gefitinib-sensitive phosphorylation of the downstream adaptor protein Shc. The activation of Akt was also inhibited by gefitinib, but only partly, suggesting a mechanism in addition to EGFR transactivation. Inhibition of PKC blocked neurotensin-induced DNA synthesis in HCT116 cells.
Conclusions: While acting predominantly through PKC in Panc-1 cells and via EGFR transactivation in HT29 cells, neurotensin used both these pathways in HCT116 cells. In these cells, neurotensin-induced activation of ERK and stimulation of DNA synthesis was PKC-dependent, whereas activation of the PI3K/Akt pathway was mediated by stimulation of metalloproteinases and subsequent transactivation of the EGFR. Thus, the data show that the signalling mechanisms mediating the effects of neurotensin involve multiple pathways and are cell-dependent.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Involvement of MAP-kinase, PI3-kinase and EGF-receptor in the stimulatory effect of Neurotensin on DNA synthesis in PC3 cells.Regul Pept. 2004 Aug 15;120(1-3):155-66. doi: 10.1016/j.regpep.2004.03.004. Regul Pept. 2004. PMID: 15177934
-
Mechanisms involved in PGE2-induced transactivation of the epidermal growth factor receptor in MH1C1 hepatocarcinoma cells.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2012 Sep 11;31(1):72. doi: 10.1186/1756-9966-31-72. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2012. PMID: 22967907 Free PMC article.
-
Neurotensin stimulates protein kinase C-dependent mitogenic signaling in human pancreatic carcinoma cell line PANC-1.Cancer Res. 2003 May 15;63(10):2379-87. Cancer Res. 2003. PMID: 12750255
-
Gastrointestinal peptide signalling in health and disease.Eur J Surg Suppl. 2002;(587):23-38. Eur J Surg Suppl. 2002. PMID: 16144198 Review.
-
Bombesin, endothelin, neurotensin and pituitary adenylate cyclase activating polypeptide cause tyrosine phosphorylation of receptor tyrosine kinases.Peptides. 2021 Mar;137:170480. doi: 10.1016/j.peptides.2020.170480. Epub 2020 Dec 29. Peptides. 2021. PMID: 33385499 Review.
Cited by
-
Acting on Hormone Receptors with Minimal Side Effect on Cell Proliferation: A Timely Challenge Illustrated with GLP-1R and GPER.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2013 Apr 29;4:50. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2013.00050. eCollection 2013. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2013. PMID: 23641235 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of EGFR, HER2 and HER3 by neurotensin/neurotensin receptor 1 renders breast tumors aggressive yet highly responsive to lapatinib and metformin in mice.Oncotarget. 2014 Sep 30;5(18):8235-51. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.1632. Oncotarget. 2014. PMID: 25249538 Free PMC article.
-
Ionic and signaling mechanisms involved in neurotensin-mediated excitation of central amygdala neurons.Neuropharmacology. 2021 Sep 15;196:108714. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2021.108714. Epub 2021 Jul 14. Neuropharmacology. 2021. PMID: 34271017 Free PMC article.
-
Stabilization of pre-existing neurotensin receptor conformational states by β-arrestin-1 and the biased allosteric modulator ML314.Nat Commun. 2023 Jun 7;14(1):3328. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-38894-8. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 37286565 Free PMC article.
-
Adding of neurotensin to non-small cell lung cancer cells increases tyrosine phosphorylation of HER3.Peptides. 2022 Oct;156:170858. doi: 10.1016/j.peptides.2022.170858. Epub 2022 Aug 3. Peptides. 2022. PMID: 35932909 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

