Comprehensive profiling of radiosensitive human cell lines with DNA damage response assays identifies the neutral comet assay as a potential surrogate for clonogenic survival
- PMID: 21962002
- PMCID: PMC4316198
- DOI: 10.1667/rr2580.1
Comprehensive profiling of radiosensitive human cell lines with DNA damage response assays identifies the neutral comet assay as a potential surrogate for clonogenic survival
Abstract
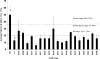
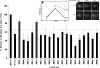
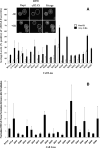
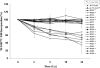
In an effort to explore the possible causes of human radiosensitivity and identify more rapid assays for cellular radiosensitivity, we interrogated a set of assays that evaluate cellular functions involved in recognition and repair of DNA double-strand breaks: (1) neutral comet assay, (2) radiation-induced γ-H2AX focus formation, (3) the temporal kinetics of structural maintenance of chromosomes 1 phosphorylation, (4) intra-S-phase checkpoint integrity, and (5) mitochondrial respiration. We characterized a unique panel of 19 "radiosensitive" human lymphoblastoid cell lines from individuals with undiagnosed diseases suggestive of a DNA repair disorder. Radiosensitivity was defined by reduced cellular survival using a clonogenic survival assay. Each assay identified cell lines with defects in DNA damage response functions. The highest concordance rate observed, 89% (17/19), was between an abnormal neutral comet assay and reduced survival by the colony survival assay. Our data also suggested that the neutral comet assay would be a more rapid surrogate for analyzing DNA repair/processing disorders.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The potential value of the neutral comet assay and the expression of genes associated with DNA damage in assessing the radiosensitivity of tumor cells.Mutat Res. 2012 Oct 9;748(1-2):52-9. doi: 10.1016/j.mrgentox.2012.06.008. Epub 2012 Jul 9. Mutat Res. 2012. PMID: 22790088
-
Relationship between DNA double-strand break rejoining and cell survival after exposure to ionizing radiation in human fibroblast strains with differing ATM/p53 status: implications for evaluation of clinical radiosensitivity.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2006 Dec 1;66(5):1498-505. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2006.08.064. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2006. PMID: 17126209
-
Relationship between clonogenic radiosensitivity, radiation-induced apoptosis and DNA damage/repair in human colon cancer cells.Br J Cancer. 2003 Dec 15;89(12):2277-83. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6601427. Br J Cancer. 2003. PMID: 14676806 Free PMC article.
-
The role of DNA single- and double-strand breaks in cell killing by ionizing radiation.Radiat Res. 1998 Nov;150(5 Suppl):S42-51. Radiat Res. 1998. PMID: 9806608 Review.
-
[Individual response to ionising radiation: What predictive assay(s) to choose?].C R Biol. 2011 Feb;334(2):140-57. doi: 10.1016/j.crvi.2010.12.018. C R Biol. 2011. PMID: 21333944 Review. French.
Cited by
-
Pathogenesis of ataxia-telangiectasia: the next generation of ATM functions.Blood. 2013 May 16;121(20):4036-45. doi: 10.1182/blood-2012-09-456897. Epub 2013 Feb 25. Blood. 2013. PMID: 23440242 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biomarkers of DNA Damage Response Enable Flow Cytometry-Based Diagnostic to Identify Inborn DNA Repair Defects in Primary Immunodeficiencies.J Clin Immunol. 2022 Feb;42(2):286-298. doi: 10.1007/s10875-021-01156-7. Epub 2021 Oct 30. J Clin Immunol. 2022. PMID: 34716846 Free PMC article.
-
Homozygous mutation of MTPAP causes cellular radiosensitivity and persistent DNA double-strand breaks.Cell Death Dis. 2014 Mar 20;5(3):e1130. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2014.99. Cell Death Dis. 2014. PMID: 24651433 Free PMC article.
-
ATM-dependent MiR-335 targets CtIP and modulates the DNA damage response.PLoS Genet. 2013 May;9(5):e1003505. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1003505. Epub 2013 May 16. PLoS Genet. 2013. PMID: 23696749 Free PMC article.
-
Dubowitz syndrome is a complex comprised of multiple, genetically distinct and phenotypically overlapping disorders.PLoS One. 2014 Jun 3;9(6):e98686. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0098686. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24892279 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zampetti-Bosseler F, Scott D. Cell death, chromosome damage and mitotic delay in normal human, ataxia telangiectasia and retinoblastoma fibroblasts after x-irradiation. Int J Radiat Biol Relat Stud Phys Chem Med. 1981;39:547–58. - PubMed
-
- Khanna KK, Jackson SP. DNA double-strand breaks: signaling, repair and the cancer connection. Nat Genet. 2001;27:247–54. - PubMed
-
- Huo YK, Wang Z, Hong JH, Chessa L, McBride WH, Perlman SL, et al. Radiosensitivity of ataxia-telangiectasia, X-linked agammaglobulinemia and related syndromes. Cancer Res. 1994;54:2544–7. - PubMed
-
- Gatti RA, Boder E, Good RA. Immunodeficiency, radiosensitivity, and the XCIND syndrome. Immunol Res. 2007;38:87–101. - PubMed
-
- Sun X, Becker-Catania SG, Chun HH, Hwang MJ, Huo Y, Wang Z, et al. Early diagnosis of ataxia-telangiectasia using radiosensitivity testing. J Pediatr. 2002;140:724–31. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

