Crystal structure of the mammalian GIRK2 K+ channel and gating regulation by G proteins, PIP2, and sodium
- PMID: 21962516
- PMCID: PMC3243363
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2011.07.046
Crystal structure of the mammalian GIRK2 K+ channel and gating regulation by G proteins, PIP2, and sodium
Abstract
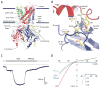
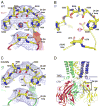
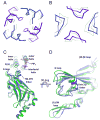
G protein-gated K(+) channels (Kir3.1-Kir3.4) control electrical excitability in many different cells. Among their functions relevant to human physiology and disease, they regulate the heart rate and govern a wide range of neuronal activities. Here, we present the first crystal structures of a G protein-gated K(+) channel. By comparing the wild-type structure to that of a constitutively active mutant, we identify a global conformational change through which G proteins could open a G loop gate in the cytoplasmic domain. The structures of both channels in the absence and presence of PIP(2) suggest that G proteins open only the G loop gate in the absence of PIP(2), but in the presence of PIP(2) the G loop gate and a second inner helix gate become coupled, so that both gates open. We also identify a strategically located Na(+) ion-binding site, which would allow intracellular Na(+) to modulate GIRK channel activity. These data provide a structural basis for understanding multiligand regulation of GIRK channel gating.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


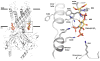
References
-
- Boudker O, Ryan RM, Yernool D, Shimamoto K, Gouaux E. Coupling substrate and ion binding to extracellular gate of a sodium-dependent aspartate transporter. Nature. 2007;445:387–393. - PubMed
-
- Clarke OB, Caputo AT, Hill AP, Vandenberg JI, Smith BJ, Gulbis JM. Domain reorientation and rotation of an intracellular assembly regulate conduction in Kir potassium channels. Cell. 2010;141:1018–1029. - PubMed
-
- Decher N, Renigunta V, Zuzarte M, Soom M, Heinemann SH, Timothy KW, Keating MT, Daut J, Sanguinetti MC, Splawski I. Impaired interaction between the slide helix and the C-terminus of Kir2.1: a novel mechanism of Andersen syndrome. Cardiovasc Res. 2007;75:748–757. - PubMed
-
- Donaldson MR, Jensen JL, Tristani-Firouzi M, Tawil R, Bendahhou S, Suarez WA, Cobo AM, Poza JJ, Behr E, Wagstaff J, et al. PIP2 binding residues of Kir2.1 are common targets of mutations causing Andersen syndrome. Neurology. 2003;60:1811–1816. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

