Multiple TGF-β superfamily signals modulate the adult Drosophila immune response
- PMID: 21962711
- PMCID: PMC3191266
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cub.2011.08.048
Multiple TGF-β superfamily signals modulate the adult Drosophila immune response
Abstract
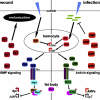
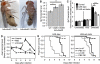
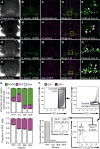
TGF-β superfamily signals play complex roles in regulation of tissue repair and inflammation in mammals [1]. Drosophila melanogaster is a well-established model for the study of innate immune function [2, 3] and wound healing [4-7]. Here, we explore the role and regulation of two TGF-β superfamily members, dawdle and decapentaplegic (dpp), in response to wounding and infection in adult Drosophila. We find that both TGF-β signals exhibit complex regulation in response to wounding and infection, each is expressed in a subset of phagocytes, and each inhibits a specific arm of the immune response. dpp is rapidly activated by wounds and represses the production of antimicrobial peptides; flies lacking dpp function display persistent, strong antimicrobial peptide expression after even a small wound. dawdle, in contrast, is activated by Gram-positive bacterial infection but repressed by Gram-negative infection or wounding; its role is to limit infection-induced melanization. Flies lacking dawdle function exhibit melanization even when uninfected. Together, these data imply a model in which the bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) dpp is an important inhibitor of inflammation following sterile injury whereas the activin-like dawdle determines the nature of the induced immune response.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
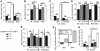

Similar articles
-
Activin and BMP Signaling Activity Affects Different Aspects of Host Anti-Nematode Immunity in Drosophila melanogaster.Front Immunol. 2021 Dec 22;12:795331. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.795331. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 35003118 Free PMC article.
-
TGF-β signaling regulates resistance to parasitic nematode infection in Drosophila melanogaster.Immunobiology. 2016 Dec;221(12):1362-1368. doi: 10.1016/j.imbio.2016.07.011. Epub 2016 Jul 25. Immunobiology. 2016. PMID: 27473342 Free PMC article.
-
lncRNA-CR46018 positively regulates the Drosophila Toll immune response by interacting with Dif/Dorsal.Dev Comp Immunol. 2021 Nov;124:104183. doi: 10.1016/j.dci.2021.104183. Epub 2021 Jun 24. Dev Comp Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34174242
-
Regulators of the Toll and Imd pathways in the Drosophila innate immune response.Trends Immunol. 2005 Apr;26(4):193-8. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2005.02.006. Trends Immunol. 2005. PMID: 15797509 Review.
-
Recognition of infectious non-self and activation of immune responses by peptidoglycan recognition protein (PGRP)-family members in Drosophila.Dev Comp Immunol. 2004 Feb;28(2):89-95. doi: 10.1016/s0145-305x(03)00121-6. Dev Comp Immunol. 2004. PMID: 12969795 Review.
Cited by
-
Of blood cells and the nervous system: hematopoiesis in the Drosophila larva.Fly (Austin). 2012 Oct-Dec;6(4):254-60. doi: 10.4161/fly.22267. Epub 2012 Sep 28. Fly (Austin). 2012. PMID: 23022764 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Altered cytokine gene expression in peripheral blood monocytes across the menstrual cycle in primary dysmenorrhea: a case-control study.PLoS One. 2013;8(2):e55200. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0055200. Epub 2013 Feb 4. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23390521 Free PMC article.
-
Aryl hydrocarbon receptor and Krüppel like factor 10 mediate a transcriptional axis modulating immune homeostasis in mosquitoes.Sci Rep. 2022 Apr 9;12(1):6005. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-09817-2. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35397616 Free PMC article.
-
Activin and BMP Signaling Activity Affects Different Aspects of Host Anti-Nematode Immunity in Drosophila melanogaster.Front Immunol. 2021 Dec 22;12:795331. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.795331. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 35003118 Free PMC article.
-
Transcript analysis reveals the involvement of NF-κB transcription factors for the activation of TGF-β signaling in nematode-infected Drosophila.Immunogenetics. 2019 Jul;71(7):501-510. doi: 10.1007/s00251-019-01119-8. Epub 2019 May 30. Immunogenetics. 2019. PMID: 31147740
References
-
- Li M.O., Wan Y.Y., Sanjabi S., Robertson A.K., Flavell R.A. Transforming growth factor-beta regulation of immune responses. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2006;24:99–146. - PubMed
-
- Brennan C.A., Anderson K.V. Drosophila: the genetics of innate immune recognition and response. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2004;22:457–483. - PubMed
-
- Lemaitre B., Hoffmann J. The host defense of Drosophila melanogaster. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2007;25:697–743. - PubMed
-
- Rämet M., Lanot R., Zachary D., Manfruelli P. JNK signaling pathway is required for efficient wound healing in Drosophila. Dev. Biol. 2002;241:145–156. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

