Multiple TGF-β superfamily signals modulate the adult Drosophila immune response
- PMID: 21962711
- PMCID: PMC3191266
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cub.2011.08.048
Multiple TGF-β superfamily signals modulate the adult Drosophila immune response
Abstract
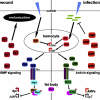
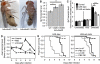
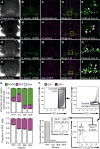
TGF-β superfamily signals play complex roles in regulation of tissue repair and inflammation in mammals [1]. Drosophila melanogaster is a well-established model for the study of innate immune function [2, 3] and wound healing [4-7]. Here, we explore the role and regulation of two TGF-β superfamily members, dawdle and decapentaplegic (dpp), in response to wounding and infection in adult Drosophila. We find that both TGF-β signals exhibit complex regulation in response to wounding and infection, each is expressed in a subset of phagocytes, and each inhibits a specific arm of the immune response. dpp is rapidly activated by wounds and represses the production of antimicrobial peptides; flies lacking dpp function display persistent, strong antimicrobial peptide expression after even a small wound. dawdle, in contrast, is activated by Gram-positive bacterial infection but repressed by Gram-negative infection or wounding; its role is to limit infection-induced melanization. Flies lacking dawdle function exhibit melanization even when uninfected. Together, these data imply a model in which the bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) dpp is an important inhibitor of inflammation following sterile injury whereas the activin-like dawdle determines the nature of the induced immune response.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
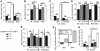

References
-
- Li M.O., Wan Y.Y., Sanjabi S., Robertson A.K., Flavell R.A. Transforming growth factor-beta regulation of immune responses. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2006;24:99–146. - PubMed
-
- Brennan C.A., Anderson K.V. Drosophila: the genetics of innate immune recognition and response. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2004;22:457–483. - PubMed
-
- Lemaitre B., Hoffmann J. The host defense of Drosophila melanogaster. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2007;25:697–743. - PubMed
-
- Rämet M., Lanot R., Zachary D., Manfruelli P. JNK signaling pathway is required for efficient wound healing in Drosophila. Dev. Biol. 2002;241:145–156. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

