Global identification of modular cullin-RING ligase substrates
- PMID: 21963094
- PMCID: PMC3226719
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2011.09.019
Global identification of modular cullin-RING ligase substrates
Erratum in
- Cell. 2012 Feb 3;148(3):620-2
Abstract
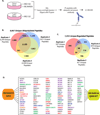
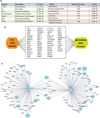
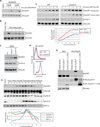
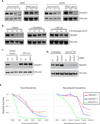
Cullin-RING ligases (CRLs) represent the largest E3 ubiquitin ligase family in eukaryotes, and the identification of their substrates is critical to understanding regulation of the proteome. Using genetic and pharmacologic Cullin inactivation coupled with genetic (GPS) and proteomic (QUAINT) assays, we have identified hundreds of proteins whose stabilities or ubiquitylation status are regulated by CRLs. Together, these approaches yielded many known CRL substrates as well as a multitude of previously unknown putative substrates. We demonstrate that one substrate, NUSAP1, is an SCF(Cyclin F) substrate during S and G2 phases of the cell cycle and is also degraded in response to DNA damage. This collection of regulated substrates is highly enriched for nodes in protein interaction networks, representing critical connections between regulatory pathways. This demonstrates the broad role of CRL ubiquitylation in all aspects of cellular biology and provides a set of proteins likely to be key indicators of cellular physiology.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



References
-
- Bai C, Sen P, Hofmann K, Ma L, Goebl M, Harper JW, Elledge SJ. SKP1 connects cell cycle regulators to the ubiquitin proteolysis machinery through a novel motif, the F-box. Cell. 1996;86:263–274. - PubMed
-
- Benanti JA, Cheung SK, Brady MC, Toczyski DP. A proteomic screen reveals SCFGrr1 targets that regulate the glycolytic-gluconeogenic switch. Nat Cell Biol. 2007;9:1184–1191. - PubMed
-
- Brownell JE, Sintchak MD, Gavin JM, Liao H, Bruzzese FJ, Bump NJ, Soucy TA, Milhollen MA, Yang X, Burkhardt AL, et al. Substrate-assisted inhibition of ubiquitin-like protein-activating enzymes: the NEDD8 E1 inhibitor MLN4924 forms a NEDD8-AMP mimetic in situ. Mol Cell. 2010;37:102–111. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

