Nitric oxide generation affects pro- and anti-angiogenic growth factor expression in primary human trophoblast
- PMID: 21963217
- PMCID: PMC3269960
- DOI: 10.1016/j.placenta.2011.08.008
Nitric oxide generation affects pro- and anti-angiogenic growth factor expression in primary human trophoblast
Abstract
Objectives: Preeclampsia is associated with reduced trophoblast placenta growth factor (PGF) expression, elevated soluble fms-like tyrosine kinase-1 (sFlt-1) and decreased bioactivity of nitric oxide (NO). Elevated sFlt-1 reduces bio-availability of PGF and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) leading to maternal endothelial dysfunction. Although NO can regulate gene expression, its ability to regulate trophoblast expression of angiogenic growth factors is not known.
Study design: Human primary term trophoblast and JEG-3 choriocarcinoma cells were cultured under 21%O(2) or 1%O(2) conditions in the presence or absence of NO donor (SNP) or inhibitor (L-NAME). Effects on PGF, VEGF and Flt-1 isoform mRNA expression were determined by quantitative real-time PCR. Changes in expression of soluble protein isoforms of FLT-1 was monitored by ELISA.
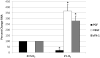
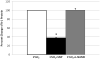
Results: Hypoxia decreased PGF mRNA but increased VEGF, sFlt-1 and Flt-1 mRNA expression in trophoblast. Generation of NO in trophoblast under 1%O(2) culture conditions significantly reversed sFlt-1 mRNA and protein expression, independent of mFlt-1. Conversely NO generation in hypoxic trophoblast increased VEGF and PGF mRNA expression.
Conclusions: NO production in primary human trophoblast cultures had divergent effects on pro-angiogenic (PGF, VEGF) versus anti-angiogenic (sFlt-1) mRNA expression, resulting in an enhanced pro-angiogenic gene expression environment in vitro.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- ACOG: ACOG practice bulletin. Diagnosis and management of preeclampsia and eclampsia Number 33, January 2002 American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 2002;77:67–75. - PubMed
-
- Gilbert JS, Ryan MJ, LaMarca BB, Sedeek M, Murphy SR, Granger JP. Pathophysiology of hypertension during preeclampsia: linking placental ischemia with endothelial dysfunction. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2008;294:H541–H550. - PubMed
-
- Levine RJ, Maynard SE, Qian C, Lim KH, England LJ, Yu KF, Schisterman EF, Thadhani R, Sachs BP, Epstein FH, Sibai BM, Sukhatme VP, Karumanchi SA. Circulating angiogenic factors and the risk of preeclampsia. N Engl J Med. 2004;350:672–83. - PubMed
-
- Levine RJ, Thadhani R, Qian C, Lam C, Lim KH, Yu KF, Blink AL, Sachs BP, Epstein FH, Sibai BM, Sukhatme VP, Karumanchi SA. Urinary placental growth factor and risk of preeclampsia. Jama. 2005;293:77–85. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

