Spatial frequency threshold and contrast sensitivity of an optomotor behavior are impaired in the Ins2Akita mouse model of diabetes
- PMID: 21963766
- PMCID: PMC3298119
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbr.2011.09.030
Spatial frequency threshold and contrast sensitivity of an optomotor behavior are impaired in the Ins2Akita mouse model of diabetes
Abstract
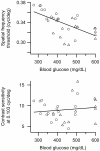
Diabetic retinopathy can lead to progressive loss of vision and is a leading cause of blindness. The Ins2(Akita) mouse model of diabetes develops significant retinal and systemic pathology, but how these affect visual behavior is unknown. Here, we show that Ins2(Akita) mice have progressive, quantifiable vision deficits in an optomotor behavior. This mouse line is a promising model in which to understand the contribution of retinal neuronal injury during the chronic hyperglycemia and hypoinsulinemia of diabetes to deficits in vision.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Fong DS, Aiello L, Gardner TW, King GL, Blankenship G, Cavallerano JD, et al. Retinopathy in diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2004;27(Suppl 1):S84–7. - PubMed
-
- Jackson GR, Barber AJ. Visual dysfunction associated with diabetic retinopathy. Curr Diab Rep. 2010;10:380–4. - PubMed
-
- Bangstad HJ, Brinchmann-Hansen O, Hultgren S, Dahl-Jorgensen K, Hanssen KF. Impaired contrast sensitivity in adolescents and young type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetic patients with microalbuminuria. Acta Ophthalmol (Copenh) 1994;72:668–73. - PubMed
-
- Parravano M, Oddone F, Mineo D, Centofanti M, Borboni P, Lauro R, et al. The role of Humphrey Matrix testing in the early diagnosis of retinopathy in type 1 diabetes. Br J Ophthalmol. 2008;92:1656–60. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

